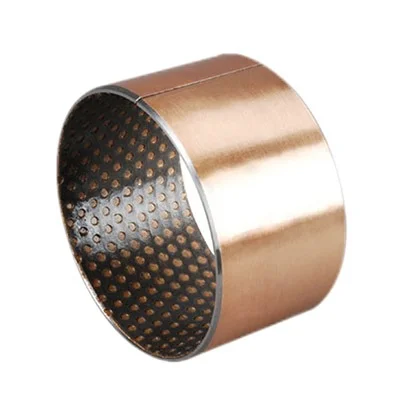
Boundary Lubrication Bushing
Boundary lubrication bearings consist of a layer of non-metallic self lubricating material (POM) that has been chemically bonded onto a layer of steel. These bushings are very resistant to wear and have a very low coefficient of friction. MW-2 bushings ensure long-lasting, efficient operation even in demanding conditions.
Table Of Contents For This Page
To make sure you can find the information you want quickly,
we have prepared this content directory that will jump to the corresponding location when you click on it.
Bushing Material
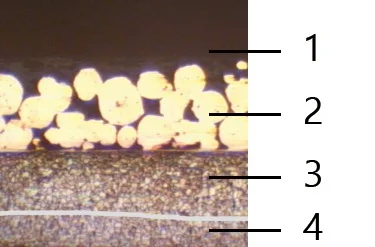
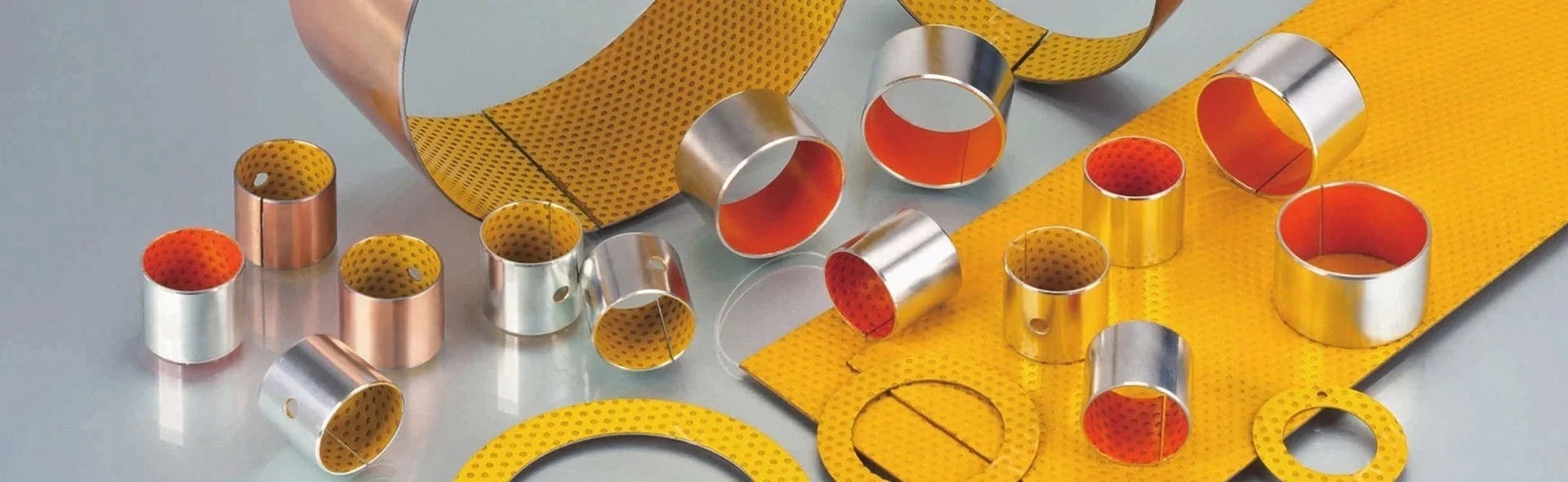
Boundary Lubrication Bushing:self-lubricating bushings consist of a high-strength, three-layer composite structure
Material Structure & Technical Details
Here are some of the common equivalents or aliases for Boundary Lubrication Bushing : SF-2 Bushing、DX Bushing、OILES 500 、IGUS G series、VIBRA series、BMZ series and Composite Bushings etc.
Materials Structure And Thickness(Metallurgied Structuer)
- Fiber-reinforced POM:0.3-0.5 mm
- Porous bronze: 0.2 -0.3 mm
- Steel backing: 0.4 -2.2 mm
- Electroplating layer: Tin-plating about 0.005 mm,or copper-plating about 0.008 mm
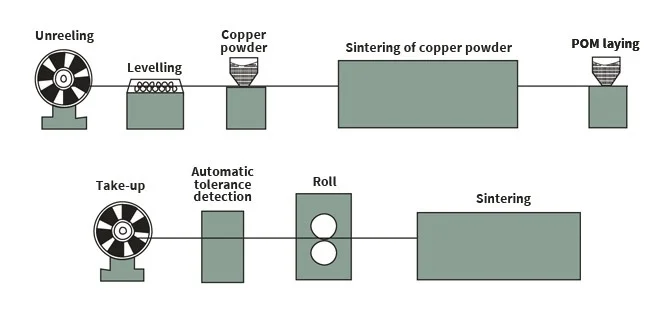
Boundary Lubrication Bushing Machining Process
The foundation of the MW-2 bushing is a high-quality low-carbon steel backing. This layer provides excellent mechanical strength and high load-bearing capacity, ensuring the bushing maintains its shape and performance under heavy loads and mechanical stress.
2.Bronze Powder Layer — Enhanced Wear Resistance and Heat Dissipation
A sintered bronze powder layer is applied over the steel backing. This layer enhances the bushing’s wear resistance and provides excellent thermal conductivity, allowing heat generated by friction to dissipate more efficiently.
3.POM (Polyoxymethylene) Layer — Low Friction and Excellent Wear Resistance
The surface of the MW-2 bushing is made from POM (Polyoxymethylene), a high-performance engineering plastic known for its excellent wear resistance and low friction properties. This layer ensures smooth, low-friction operation, even under medium loads, and provides self-lubrication throughout the product’s life cycle.
Material Combination

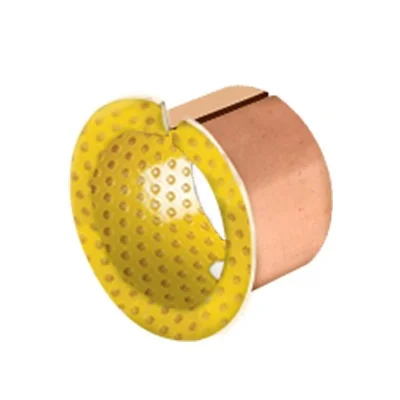
Copper black
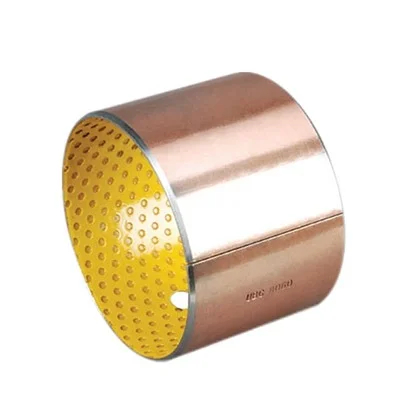

Copper yellow
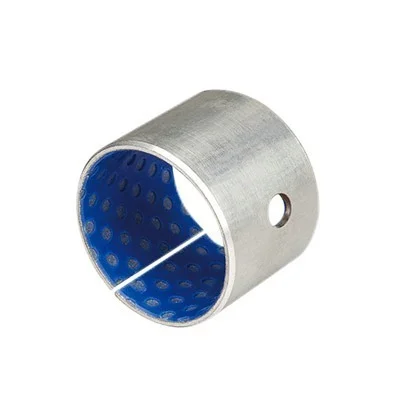

Tin blue
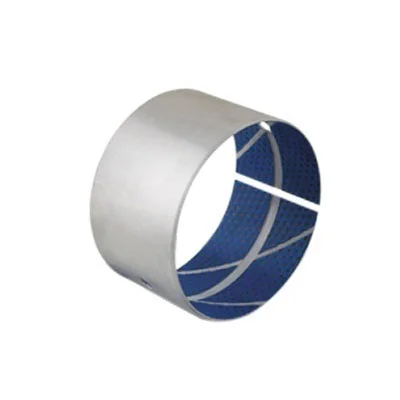

Oil groove
| Type | Application Characteristic | Sinter Bronze | Backing | Lining |
| MW-2X | General,lead free | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+Pb+Graphite+Other |
| MW-2Y | Lead free | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+Fibre+Other |
| MW-2S | For Oilless Lubricating of short time | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+PTFE+Other |
| MW-2L | Lower Friction coef. | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+Fibre+Other |
Bushing Size

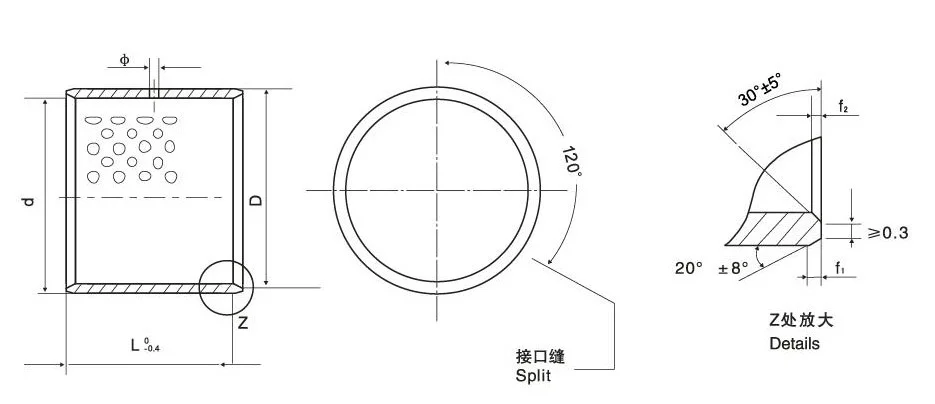
| d | D | ( shaft dia.) | (housing bore H7) | Wall thickness | (hole dia.) | f₁ | f₂ | L040 | ||||||||||
| 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |||||||||
| min. | max. | |||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 12 | 10 | 12 | 0.955 | 0.980 | 4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1010 | 1015 | 1020 | |||||||
| 12 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 1210 | 1212 | 1215 | 1220 | ||||||||||
| 14 | 16 | 14 | 16 | 4 | 1412 | 1415 | 1420 | |||||||||||
| 15 | 17 | 15 | 17 | 4 | 1512 | 1515 | 1520 | 1525 | ||||||||||
| 16 | 18 | 16 | 18 | 4 | 1615 | 1620 | 1625 | |||||||||||
| 18 | 20 | 18 | 20 | 4 | 1815 | 1820 | 1825 | |||||||||||
| 20 | 23 | 20 | 23 | 1.445 | 1.475 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 2015 | 2020 | 2025 | 2030 | ||||||
| 22 | 25 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 2215 | 2225 | ||||||||||||
| 25 | 28 | 25 | 28 | 6 | 2220 | 2525 | 2530 | |||||||||||
| 28 | 32 | 28 | 32 | 1.935 | 1.970 | 6 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 2220 | 2830 | ||||||||
| 30 | 34 | 30 | 34 | 6 | 3020 | 3025 | 3030 | 3040 | ||||||||||
| 35 | 39 | 35 | 39 | 6 | 3520 | 3530 | 3535 | 3540 | ||||||||||
| 40 | 44 | 40 | 44 | 8 | 4020 | 4030 | 4040 | 4050 | ||||||||||
| 45 | 50 | 45 | 50 | 2.415 | 2.460 | 8 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 4520 | 4530 | 4540 | 4545 | 4550 | |||||
| 50 | 55 | 50 | 55 | 8 | 5030 | 5040 | 5050 | |||||||||||
| 55 | 60 | 55 | 60 | 8 | 5530 | 5540 | 5550 | |||||||||||
| 60 | 65 | 60 | 65 | 8 | 6030 | 6040 | 6050 | |||||||||||
Bushing Shape
The different bushing shapes allow bushings to be widely used in various mechanical structure parts, such as the moving parts inside cars or the connecting parts on industrial machinery or other situations where there’s friction and wear that needs to be beaten down.

Cylindrical

Flanged
Thrust Washers
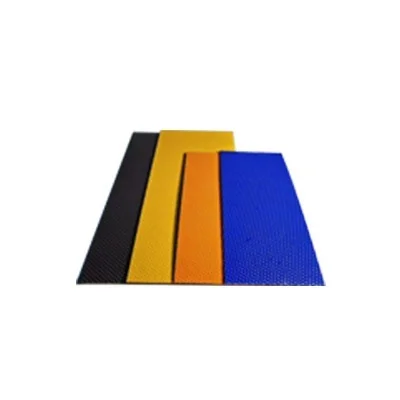

Wear Plates
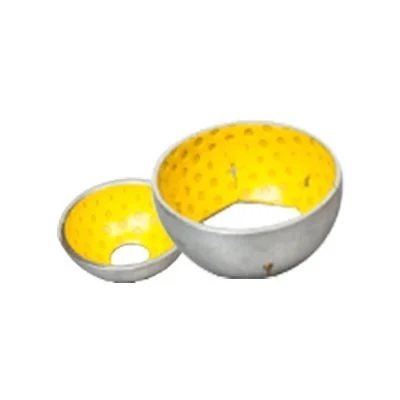

Special Shape
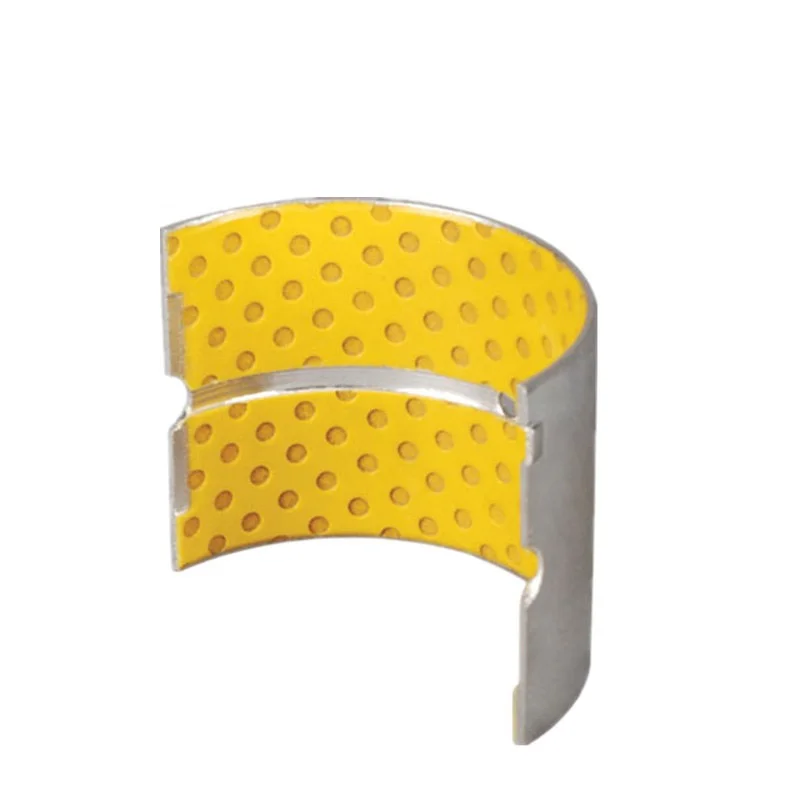

Bearing Bush
Key Advantages of MW-2 Self-Lubricating Bushings
Self-Lubricating, Cost-Saving Solution
The POM layer in MW-2 bushings provides long-term self-lubrication, reducing or eliminating the need for external lubricants. This significantly lowers equipment maintenance costs, reduces the need for frequent lubrication, and extends the lifespan of machinery.
High Wear Resistance for Harsh Operating Conditions
The durable materials and multi-layer structure of MW-2 bushings allow them to withstand tough working environments (dust, dirt, high humidity, etc.). Whether in hydraulic equipment under high pressure or construction machinery operating under heavy loads, MW-2 bushings deliver outstanding wear resistance.
Reduced Downtime, Increased Productivity
For B2B customers, minimizing downtime is crucial to reducing production costs and maximizing efficiency. MW-2 bushings’ durable and long-lasting design significantly reduces downtime caused by maintenance or part replacements, ensuring that your production process runs smoothly.
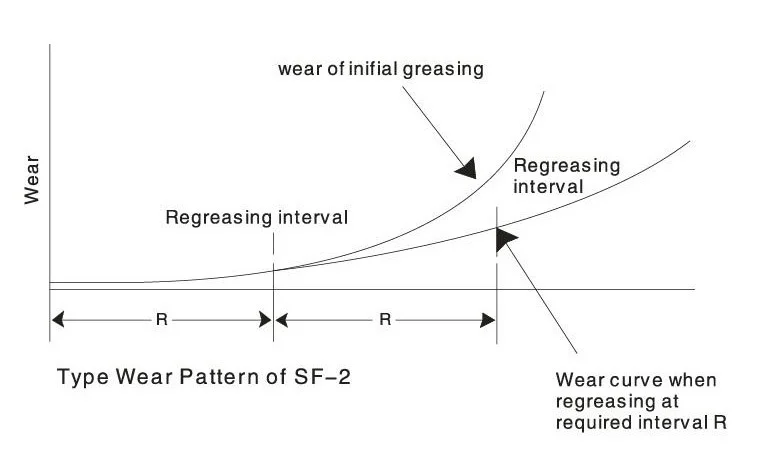
Technical Specifications
To meet the diverse requirements of various applications, MW-2 self-lubricating bushings are designed and manufactured with precise material ratios and processes to ensure optimal performance.
- Material Structure: Low-carbon steel + sintered bronze powder + POM (Polyoxymethylene)
- Max Static Load: 140N/mm²
- Coefficient of Friction: 0.05-0.20 (depending on the working conditions)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +130°C
- Max Sliding Speed: 2.5m/s
- Wear Rate: High wear resistance under normal operating conditions, suitable for medium load and low-speed applications

Bushing Applications
Versatile Applications for Various Equipment
Construction Machinery: Excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and other equipment that require high-load and self-lubricating parts.
Agricultural Machinery: Harvesters, tractors, and other equipment in need of wear-resistant bearing solutions.
Automotive Industry: Suspension systems, steering components, and other parts that require self-lubrication and wear resistance.
Hydraulic Systems: Guiding and sealing applications in hydraulic cylinders and piston rods that require lubrication and wear protection.

Combine Harvester

Crane

Bulldozer

Loader

Graders

Automobile

Truck

Tractor

Dump Truck

Excavator
Custom Services and Solutions
Personalized Design Support
We understand that each customer’s needs may vary, which is why we offer customized solutions tailored to different equipment applications. We provideself-lubricating bushings in specific sizes, materials, and thicknesses to match your unique requirements. No matter what industry or application your equipment is used in, we can offer the optimal product selection to meet your needs.
Free consultation
Communicate with us to clarify the requirements
Free design
Customize your product according to your needs
Sample making
Confirm the drawings and arrange for sampling
Sample confirmation
Customer confirms sample and arranges production
Finished inspection
Inspect the finished product and arrange for shipment
More Related Bushing products
Contact Us for More Information
We not only provide high-quality self-lubricating bushings but also offer comprehensive technical support and after-sales service to ensure your equipment always operates at peak performance. If you have any questions or need a quote, please feel free to contact us at any time.
Tel/Whatsapp: +86 136 4583 4002
Email:ivan@mybushing.com





