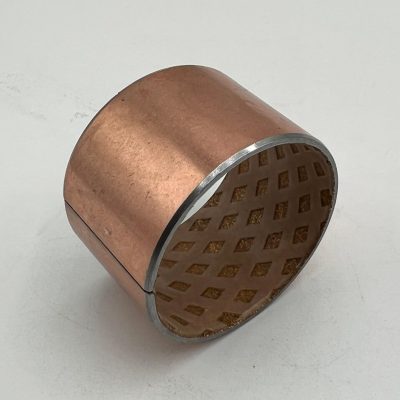
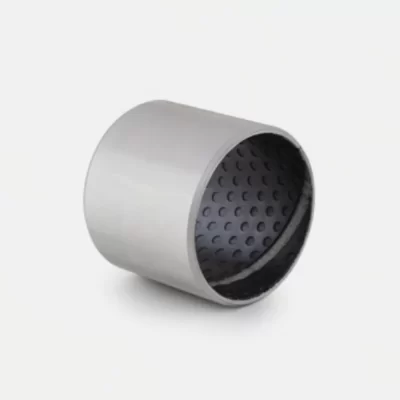
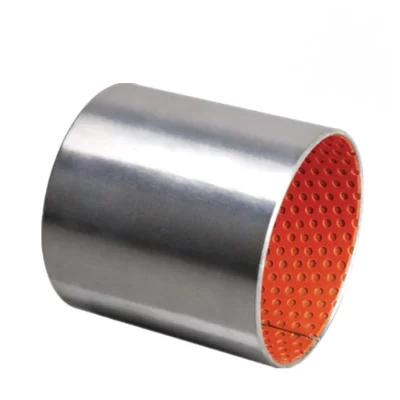
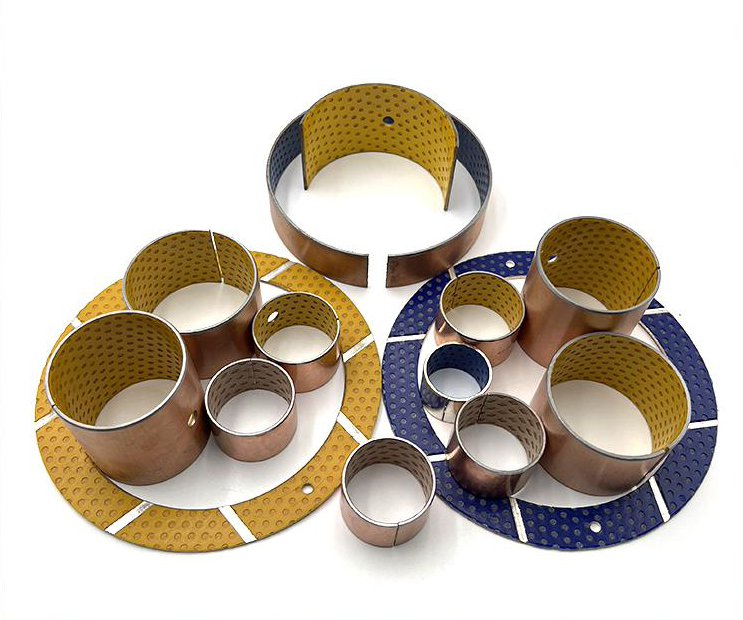
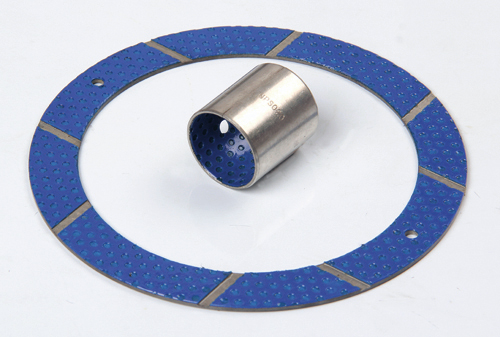
MYWAY DX/SF-2 Boundary Lubricating Bushing
A Professional Solution for Your Equipment’s Wear Resistance and Self-Lubrication Needs.
Reliable performance tailored for various industrial machinery and equipment applications.
Home » DX/SF-2 Boundary Lubricating Bushing
DX/SF-2 Boundary Lubricating Bushing

What is Boundary Lubricating Bushing?
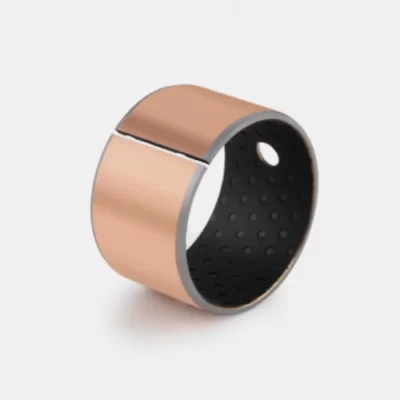
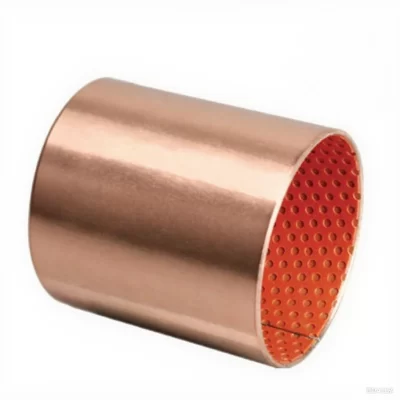
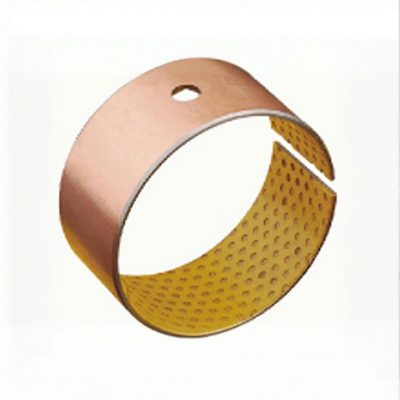
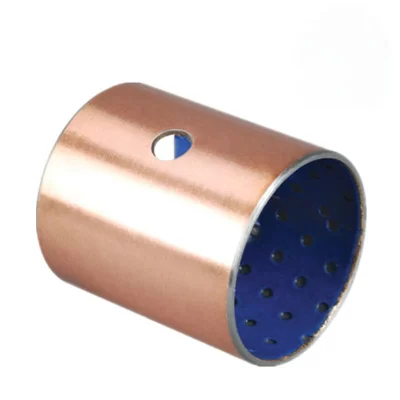
Crafted from high-quality low-carbon steel, copper powder, and modified POM via specialized processes, this self-lubricating bearing delivers exceptional performance under medium-to-high load and low-speed conditions. The steel base provides robust load-bearing capacity and efficient heat transfer, while the sintered copper powder layer enhances wear resistance and heat dissipation. The modified POM surface incorporates evenly distributed oil pockets for optimal lubricant distribution—initial lubrication is recommended. Designed for long-term, maintenance-free operation in boundary lubrication environments, occasional relubrication significantly extends service life. Ideal for rotary and oscillating motions with high load and low speed.
Boundary Lubricating Bushings by Structure
Boundary Lubricating Bushings by Material
Boundary Lubricating Bushings by Type
Which Specification Do You Need?
Plain Bushing
| Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. |
| 0805 | 10×8×5 | 1108 | 13×11×8 | 1410 | 16×14×10 | 1620 | 18×16×20 | 2012 | 23×20×12 | 2410 | 27×24×10 |
| 0806 | 10×8×6 | 1109 | 13×11×9 | 1412 | 16×14×12 | 1625 | 18×16×25 | 2015 | 23×20×15 | 2412 | 27×24×12 |
| 0808 | 10×8×8 | 1110 | 13×11×10 | 1415 | 16×14×15 | 1708 | 19×17×8 | 2020 | 23×20×20 | 2415 | 27×24×15 |
| 0810 | 10×8×10 | 1112 | 13×11×12 | 1420 | 16×14×20 | 1710 | 19×17×10 | 2025 | 23×20×25 | 2420 | 27×24×20 |
| 0812 | 10×8×12 | 1206 | 14×12×6 | 1422 | 16×14×22 | 1712 | 19×17×12 | 2030 | 23×20×30 | 2425 | 27×24×25 |
| 0815 | 10×8×15 | 1208 | 14×12×8 | 1425 | 16×14×25 | 1715 | 19×17×15 | 2035 | 23×20×35 | 2428 | 27×24×28 |
| 0820 | 10×8×20 | 1210 | 14×12×10 | 1508 | 17×15×8 | 1718 | 19×17×18 | 2040 | 23×20×10 | 2430 | 27×24×30 |
| 0908 | 11×9×8 | 1212 | 14×12×12 | 1510 | 17×15×10 | 1720 | 19×17×20 | 2210 | 25×22×10 | 2432 | 27×24×32 |
| 0909 | 11×9×9 | 1214 | 14×12×14 | 1512 | 17×15×12 | 1725 | 19×17×25 | 2212 | 25×22×12 | 2435 | 27×24×35 |
| 0910 | 11×9×10 | 1215 | 14×12×15 | 1515 | 17×15×15 | 1808 | 20×18×8 | 2215 | 25×22×15 | 2438 | 27×24×38 |
| 1005 | 12×10×5 | 1216 | 14×12×16 | 1518 | 17×15×18 | 1810 | 20×18×10 | 2220 | 25×22×20 | 2440 | 27×24×40 |
| 1006 | 12×10×6 | 1220 | 14×12×20 | 1520 | 17×15×20 | 1812 | 20×18×12 | 2225 | 25×22×25 | 2450 | 27×24×50 |
| 1008 | 12×10×8 | 1225 | 14×12×25 | 1525 | 17×15×25 | 1815 | 20×18×15 | 2230 | 25×22×30 | 2510 | 28×25×10 |
| 1009 | 12×10×9 | 1308 | 15×13×8 | 1608 | 18×16×8 | 1820 | 20×18×20 | 2235 | 25×22×35 | 2512 | 28×25×12 |
| 1010 | 12×10×10 | 1309 | 15×13×9 | 1610 | 18×16×10 | 1825 | 20×18×25 | 2238 | 25×22×38 | 2515 | 28×25×15 |
| 1012 | 12×10×12 | 1310 | 15×13×10 | 1612 | 18×16×12 | 1830 | 20×18×30 | 2240 | 25×22×40 | 2520 | 28×25×20 |
| 1015 | 12×10×15 | 1312 | 15×13×12 | 1615 | 18×16×15 | 2008 | 23×20×8 | 2245 | 25×22×45 | 2525 | 28×25×25 |
| 1020 | 12×10×20 | 1315 | 15×13×15 | 1618 | 18×16×18 | 2010 | 23×20×10 | 2250 | 25×22×50 | …… | …… |
Flange Bushing
| Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. |
| 0303 | 7/4.6×3×3.8 | 1206 | 20/14×12×7 | 1820 | 26/20×18×21 | 2525 | 36/28×25×26.5 | 3525 | 49/39×35×27 |
| 0404 | 9/5.6×4×4.8 | 1208 | 20/14×12×9 | 2010 | 31/23×20×11.5 | 2615 | 38/30×26×17 | 3530 | 49/39×35×32 |
| 0504 | 10/7×5×5 | 1210 | 20/14×12×11 | 2012 | 31/23×20×13.5 | 2620 | 38/30×26×22 | 3540 | 49/39×35×42 |
| 0505 | 10/7×5×6 | 1212 | 20/14×12×13 | 2015 | 31/23×20×16.5 | 2812 | 40/32×28×14 | 3820 | 52/42×38×22 |
| 0605 | 12/8×6×6 | 1215 | 20/14×12×16 | 2020 | 31/23×20×21.5 | 2815 | 40/32×28×17 | 4012 | 54/44×40×14 |
| 0606 | 12/8×6×7 | 1410 | 22/16×14×11 | 2025 | 31/23×20×26.5 | 2820 | 40/32×28×22 | 4020 | 54/44×40×22 |
| 0607 | 12/8×6×8 | 1412 | 22/16×14×13 | 2210 | 33/25×22×11.5 | 3012 | 42/34×30×14 | 4025 | 54/44×40×27 |
| 0705 | 13/9×7×6 | 1415 | 22/16×14×16 | 2212 | 33/25×22×13.5 | 3015 | 42/34×30×17 | 4030 | 54/44×40×32 |
| 0707 | 13/9×7×8 | 1510 | 23/17×15×11 | 2215 | 33/25×22×16.5 | 3020 | 42/34×30×22 | 4040 | 54/44×40×42 |
| 0806 | 15/10×8×7 | 1512 | 23/17×15×13 | 2220 | 33/25×22×21.5 | 3025 | 42/34×30×27 | 4520 | 60/50×45×22.5 |
| 0808 | 15/10×8×9 | 1515 | 23/17×15×16 | 2415 | 35/27×24×16.5 | 3030 | 42/34×30×32 | 4525 | 60/50×45×27.5 |
| 1006 | 18/12×10×7 | 1520 | 23/17×15×21 | 2420 | 35/27×24×21.5 | 3125 | 45/35×31×27 | 4530 | 60/50×45×32.5 |
| 1007 | 18/12×10×8 | 1615 | 24/18×16×16 | 2425 | 35/27×24×26.5 | 3220 | 46/36×32×22 | 4540 | 60/50×45×42.5 |
| 1008 | 18/12×10×9 | 1620 | 24/18×16×21 | 2510 | 36/28×25×11.5 | 3225 | 46/36×32×27 | 5020 | 65/55×50×22.5 |
| 1010 | 18/12×10×11 | 1810 | 26/20×18×11 | 2512 | 36/28×25×13.5 | 3230 | 46/36×32×32 | 5030 | 65/55×50×32.5 |
| 1012 | 18/12×10×13 | 1812 | 26/20×18×13 | 2515 | 36/28×25×16.5 | 3512 | 49/39×35×14 | 5040 | 65/55×50×42.5 |
| 1015 | 18/12×10×16 | 1815 | 26/20×18×16 | 2520 | 36/28×25×21.5 | 3520 | 49/39×35×22 | …… | …… |
Thrust Washer
| Type | Spec | Type | Spec |
| DP10 | 20×10×1.5 | DP26 | 44×26×1.5 |
| DP12 | 24×12×1.5 | DP28 | 48×28×1.5 |
| DP14 | 26×14×1.5 | DP32 | 54×32×1.5 |
| DP16 | 30×16×1.5 | DP36 | 62×38×1.5 |
| DP18 | 32×18×1.5 | DP42 | 66×42×1.5 |
| DP20 | 36×20×1.5 | DP48 | 74×48×2 |
| DP22 | 38×22×1.5 | DP52 | 78×52×2 |
| DP24 | 42×24×1.5 | DP62 | 90×62×2 |
MYWAY products can be tailored to your specific requirements.
Direct Replacements For
| Brand | Series/Models |
|---|---|
| GGB | DX, DX10, DS |
| SKF | POM, Composite Bushings |
| DAIDYNE | DBB01, DBX01 |
| PTI | PAP, P20 |
| ISB | SF-2 |
| GLT | POM-MET |
| DE | DEX, WICO |
| Daemar | THXD |
Applications of Boundary Lubricating Bushing
Versatile Applications for Various Equipment
Construction Machinery: Excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and other equipment that require high-load and self-lubricating parts.
Agricultural Machinery: Harvesters, tractors, and other equipment in need of wear-resistant bearing solutions.
Automotive Industry: Suspension systems, steering components, and other parts that require self-lubrication and wear resistance.
Hydraulic Systems: Guiding and sealing applications in hydraulic cylinders and piston rods that require lubrication and wear protection.
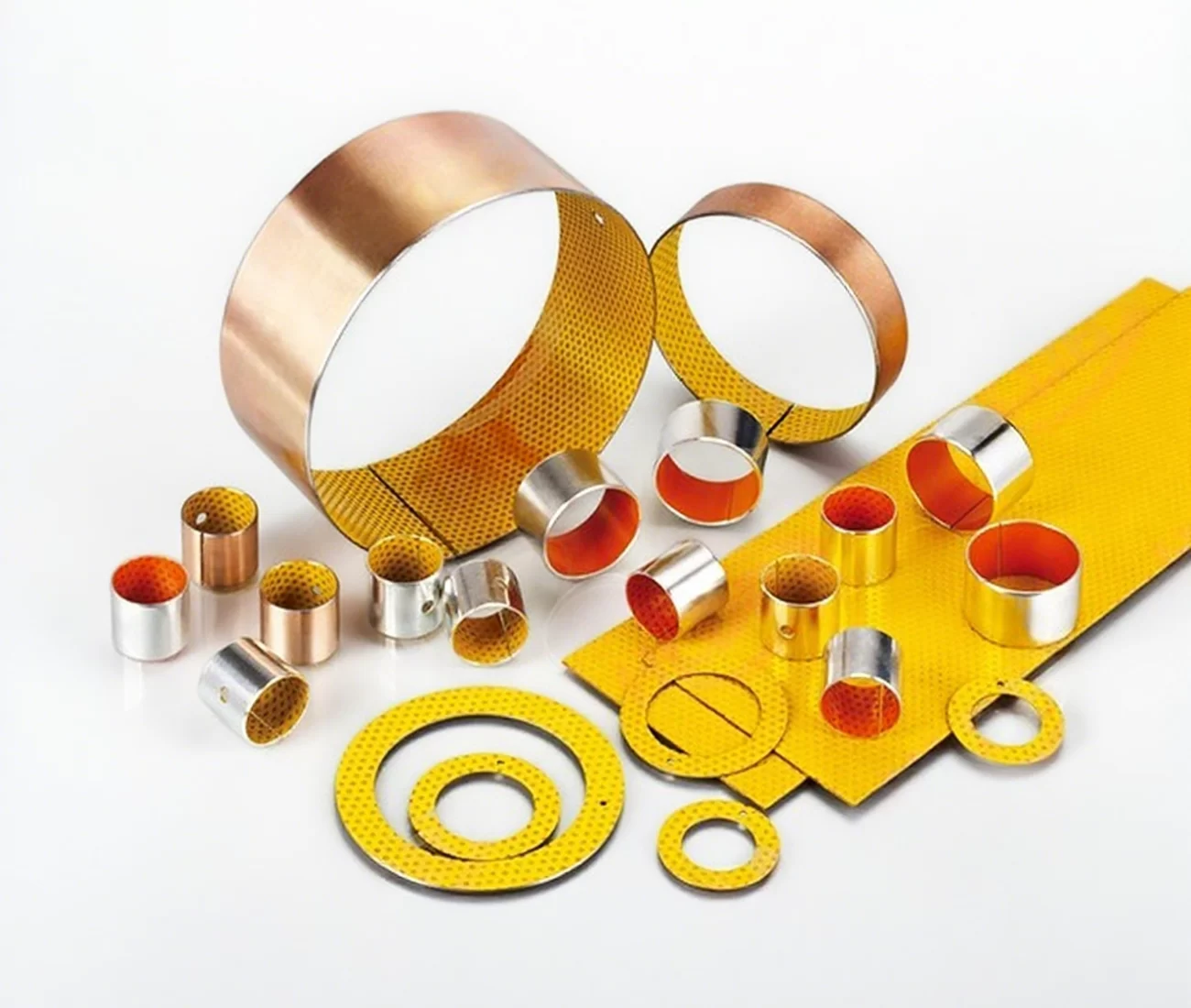
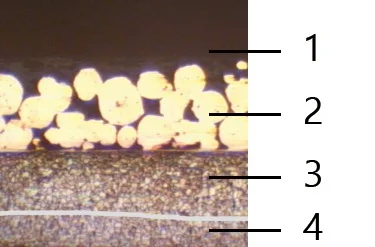
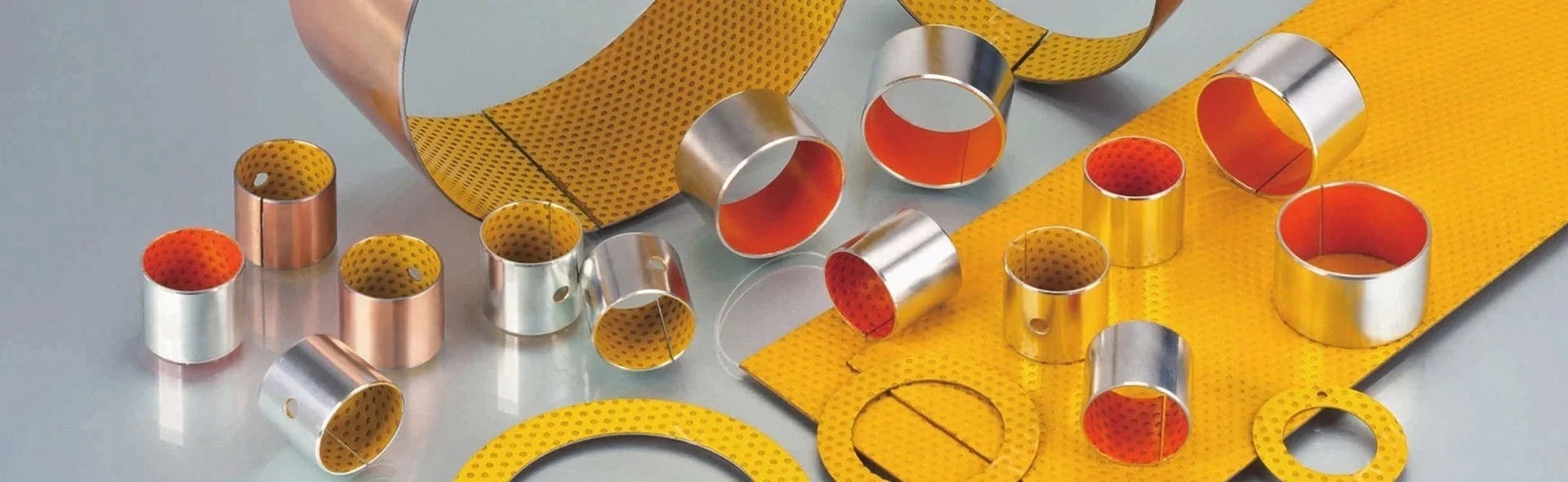
Boundary Lubrication Bushing:self-lubricating bushings consist of a high-strength, three-layer composite structure
Material Structure & Technical Details
Here are some of the common equivalents or aliases for Boundary Lubrication Bushing : SF-2 Bushing、DX Bushing、OILES 500 、IGUS G series、VIBRA series、BMZ series and Composite Bushings etc.
Materials Structure And Thickness(Metallurgied Structuer)
- Fiber-reinforced POM:0.3-0.5 mm
- Porous bronze: 0.2 -0.3 mm
- Steel backing: 0.4 -2.2 mm
- Electroplating layer: Tin-plating about 0.005 mm,or copper-plating about 0.008 mm
Boundary Lubrication Bushing Machining Process
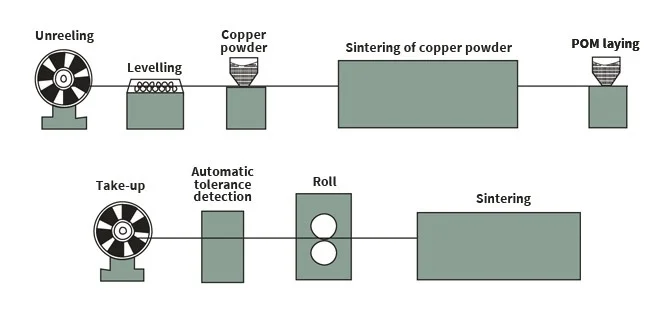
The foundation of the DX/SF-2 bushing is a high-quality low-carbon steel backing. This layer provides excellent mechanical strength and high load-bearing capacity, ensuring the bushing maintains its shape and performance under heavy loads and mechanical stress.
2.Bronze Powder Layer — Enhanced Wear Resistance and Heat Dissipation
A sintered bronze powder layer is applied over the steel backing. This layer enhances the bushing’s wear resistance and provides excellent thermal conductivity, allowing heat generated by friction to dissipate more efficiently.
3.POM (Polyoxymethylene) Layer — Low Friction and Excellent Wear Resistance
The surface of the DX/SF-2 bushing is made from POM (Polyoxymethylene), a high-performance engineering plastic known for its excellent wear resistance and low friction properties. This layer ensures smooth, low-friction operation, even under medium loads, and provides self-lubrication throughout the product’s life cycle.
Boundary Lubrication Bushing Material Combination
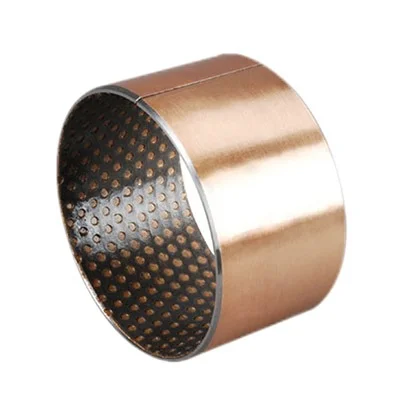

Copper black
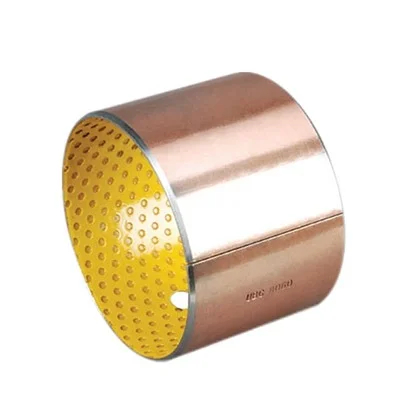

Copper yellow
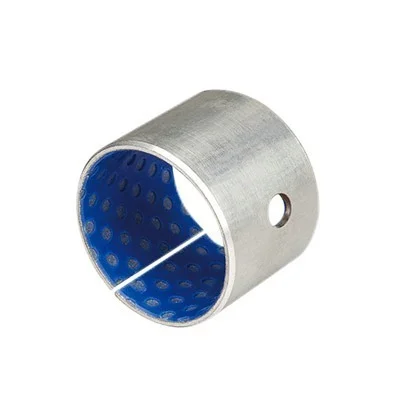

Tin blue
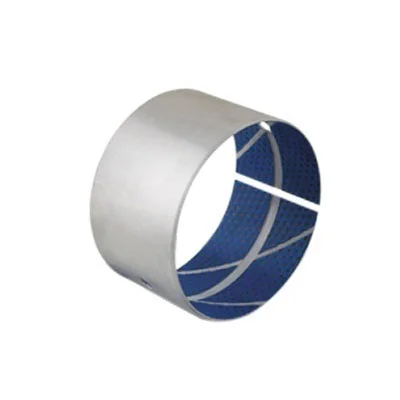

Oil groove
| Application Characteristic | Sinter Bronze | Backing | Lining |
| General,lead free | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+Pb+Graphite+Other |
| Lead free | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+Fibre+Other |
| For Oilless Lubricating of short time | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+PTFE+Other |
| Lower Friction coef. | CuSn8Zn3 | SPCC or DC01 | POB+Fibre+Other |
Key Advantages of Boundary Lubrication Bushing
Self-Lubricating, Cost-Saving Solution
The POM layer in DX/SF-2 bushings provides long-term self-lubrication, reducing or eliminating the need for external lubricants. This significantly lowers equipment maintenance costs, reduces the need for frequent lubrication, and extends the lifespan of machinery.
High Wear Resistance for Harsh Operating Conditions
The durable materials and multi-layer structure of DX/SF-2 bushings allow them to withstand tough working environments (dust, dirt, high humidity, etc.). Whether in hydraulic equipment under high pressure or construction machinery operating under heavy loads, DX/SF-2 bushings deliver outstanding wear resistance.
Reduced Downtime, Increased Productivity
For B2B customers, minimizing downtime is crucial to reducing production costs and maximizing efficiency. DX/SF-2 bushings’ durable and long-lasting design significantly reduces downtime caused by maintenance or part replacements, ensuring that your production process runs smoothly.
Technical Specifications
To meet the diverse requirements of various applications, DX/SF-2 self-lubricating bushings are designed and manufactured with precise material ratios and processes to ensure optimal performance.
- Material Structure: Low-carbon steel + sintered bronze powder + POM (Polyoxymethylene)
- Max Static Load: 140N/mm²
- Coefficient of Friction: 0.05-0.20 (depending on the working conditions)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +130°C
- Max Sliding Speed: 2.5m/s
- Wear Rate: High wear resistance under normal operating conditions, suitable for medium load and low-speed applications

Boundary Lubrication Bushings: The Complete Guide to Self-Lubricating Engineering Solutions
Introduction to Boundary Lubrication Bushings
Boundary Lubrication Bushings represent a significant advancement in bearing technology, specifically engineered to operate effectively in conditions where lubrication is minimal or intermittent. These specialized metal polymer marginal lubricating bushings fill the crucial gap between fully lubricated and completely dry sliding bearings, offering reliable performance where traditional bearings would fail.
The term “boundary lubrication” refers to the critical condition where the lubricant film is too thin to completely separate the moving surfaces, resulting in occasional metal-to-metal contact. This typically occurs during startup, shutdown, or under extreme load conditions. Boundary Lubrication POM Bushings are precisely designed to excel in these challenging circumstances, providing consistent performance and extended service life across numerous industrial applications.
Understanding the Three-Layer Composite Structure
Advanced Material Architecture
The exceptional performance of Three-Layer Composite Bushing systems stems from their sophisticated material composition:
Steel Backing Layer
The foundation consists of high-quality, low-carbon steel plate, typically copper-plated for enhanced corrosion resistance. This layer provides the structural integrity necessary to withstand heavy loads and maintain dimensional stability under pressure. The steel backing ensures the bushing can handle static loads up to 250 N/mm² and dynamic loads up to 140 N/mm², making it suitable for demanding applications.
Porous Bronze Sintered Layer
The intermediate layer consists of sintered bronze particles, creating a porous matrix that serves multiple functions. This structure facilitates superior heat conductivity, effectively dissipating frictional heat away from the sliding surface. The porosity enables mechanical interlocking with the POM layer, ensuring strong bonding between layers. Additionally, this bronze layer acts as a reservoir for lubricants in some designs, though this function is secondary in boundary lubrication applications.
POM Glide Layer
The working surface consists of Polyoxymethylene (POM), a high-performance engineering thermoplastic renowned for its excellent mechanical properties. With a typical thickness of 0.3-0.5mm, this layer provides the actual bearing surface. The distinctive yellow color of many POM layers comes from additives that enhance performance characteristics. The surface features precisely engineered lubrication pockets that gradually release lubricant during operation, maintaining the boundary lubrication film.
Technical Performance Characteristics
Exceptional Mechanical Properties
Self-Lubricating Capabilities
The composite self-lubricating bushing design incorporates lubrication reservoirs within the POM layer that serve as micro-suppliers of lubricant during operation. These pockets are designed to maintain optimal lubrication conditions at the interface between the bushing and shaft, significantly reducing friction and wear even when external lubrication is unavailable.
Load Capacity and Durability
The robust construction enables these bushings to withstand substantial mechanical stresses.
These specifications make POM-coated bushings suitable for heavy-duty applications in construction, agriculture, and industrial machinery where high loads are common.
Thermal Performance
The composite structure provides excellent thermal characteristics.
Friction and Wear Characteristics
The friction coefficients vary based on lubrication conditions:
The low friction values, combined with POM’s natural wear resistance, ensure extended service life even under challenging conditions.
Applications Across Industries
Heavy Machinery and Equipment
Agricultural and Forestry Machinery
Marginal lubricating bushings excel in agricultural equipment where contamination from dirt, dust, and moisture is inevitable. Applications include tractor implements, harvesting machinery, and processing equipment where regular maintenance is challenging.
Construction Equipment
In construction machinery, semi-solid lubricated bushings provide reliable performance in hydraulic cylinder applications, boom arms, and articulation points.
Industrial Applications
Hydraulic Systems
The DX bush variants are extensively used in hydraulic cylinders and systems where space constraints and reliability are critical.
Automotive Systems
Oilless bushings with POM surface find numerous applications in automotive systems, particularly in chassis components, steering linkages, and suspension elements.
Specialized Industrial Equipment
Food processing machinery; Textile manufacturing equipment; Medical equipment; Packaging machinery
Design and Selection Considerations
Proper Installation Guidelines
Shaft Requirements
For optimal performance, specific shaft specifications should be followed:
Surface roughness: Ra 0.4-0.8 μm
Hardness: 180-600 HB
Tolerance: h7 to h8
Surface finish: Ground or hard-turned for best results
Housing Design
Housing specifications significantly impact performance:
Housing tolerance: H7
Adequate wall thickness to support press-fit installation
Proper seating surface finish and geometry
Consideration for thermal expansion characteristics
Installation Techniques
Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance:
Use of arbor presses for controlled installation force
Avoidance of hammering directly on bushing surfaces
Ensuring proper alignment during installation
Verification of final dimensions post-installation
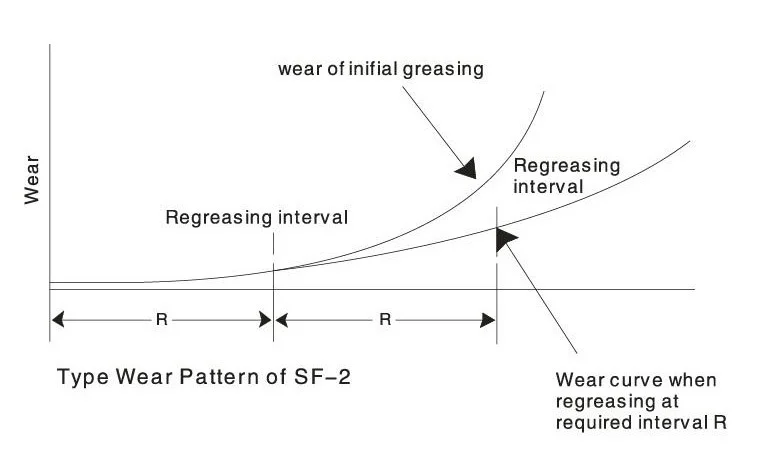
Lubrication Strategies
While designed for boundary lubrication conditions, proper initial lubrication significantly enhances performance and service life:
Initial Lubrication
Fill lubrication pockets completely before assembly
Use compatible greases (avoid those containing MoS2 or graphite)
Ensure even distribution across the entire surface
Consider application-specific lubricant selection
Maintenance Lubrication
Although designed for minimal maintenance, periodic lubrication can extend service life in demanding applications. The frequency depends on operating conditions, load cycles, and environmental factors.
Comparative Performance Analysis
Advantages Over Traditional Bushings
Compared to Bronze Bushings
Reduced maintenance requirements: Up to 3x longer service intervals
Better performance in contaminated environments
Lower friction coefficients
Superior emergency running properties
Compared to Plastic Bushings
Higher load capacity
Better heat dissipation
Improved dimensional stability
Wider temperature range capability
Performance Metrics
Case studies demonstrate significant advantages:
60% reduction in wear rates compared to traditional bronze bushings
3x extension of maintenance intervals in hydraulic cylinder applications
40% improvement in service life in contaminated environments
Reduced total cost of ownership through decreased maintenance and downtime
Technical Specifications and Standards
Comprehensive Performance Data
Material Specifications
Steel backing: Low-carbon steel, copper-plated
Sintered bronze layer: 20-30% porosity
POM layer thickness: 0.3-0.5 mm
Overall wall thickness: Standard and custom options available
Operating Parameters
Maximum sliding speed (lubricated): 5 m/s
Maximum sliding speed (unlubricated): 2.5 m/s
PV limit (lubricated): 2.8 N/mm² × m/s
Temperature range: -40°C to +130°C
Standard Compliance
DIN 1494 and ISO 3547 standards
RoHS compliant materials available
Custom specifications for specialized applications
Customization and Special Applications
Tailored Solutions
Geometric Variations
Rolled POM liner bushings for specific installation requirements
Flange bushings for axial location
Special lengths and diameters for unique applications
Custom wall thicknesses for specific load conditions
Material Modifications
Alternative POM formulations for specific chemical resistance
Special coatings for enhanced corrosion protection
Modified bronze compositions for improved performance
Custom lubrication pocket patterns
Application-Specific Designs
Elongated holes for adjustment capabilities
Special lubrication grooves and channels
Unique mounting configurations
Integrated sealing arrangements
Future Developments and Trends
Emerging Technologies
The future of boundary lubrication technology continues to evolve with several promising developments:
Advanced Material Combinations
Research continues into enhanced POM formulations and alternative polymer matrices that offer improved temperature resistance, lower friction coefficients, and enhanced wear characteristics. Nanocomposite additives show particular promise for next-generation materials.
Smart Bushing Technologies
Integration of sensor technologies and condition monitoring capabilities represents an emerging trend. These intelligent bushings can provide real-time data on wear status, temperature, and lubrication condition, enabling predictive maintenance strategies.
Environmental Considerations
The ongoing development of more environmentally friendly materials and processes continues to be a focus. This includes bio-based polymers, improved recycling capabilities, and reduced environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Conclusion
Boundary Lubrication Bushings represent a sophisticated engineering solution for challenging lubrication conditions. The three-layer composite bushing technology combines the mechanical strength of metals with the self-lubricating properties of advanced polymers, creating a reliable solution for numerous industrial applications.
From DX bush configurations in compact spaces to heavy-duty POM-coated bushings in construction equipment, these components continue to prove their value across industries. Their ability to operate effectively with minimal maintenance, withstand contaminated environments, and provide consistent performance under boundary lubrication conditions makes them indispensable in modern mechanical design.
Boundary Lubrication Bushing FAQs
1. What exactly is boundary lubrication and why is it important?
Boundary lubrication refers to the condition where the lubricant film is insufficient to completely separate moving surfaces, resulting in occasional metal-to-metal contact. This condition commonly occurs during startup, shutdown, or under heavy loads. Boundary Lubrication Bushings are specifically engineered to perform reliably under these challenging conditions, providing protection against wear and seizure when full fluid film lubrication cannot be maintained.
2. How do POM bushings compare to PTFE-based bushings in terms of performance?
While both offer self-lubricating properties, POM-coated bushings generally provide higher mechanical strength and better wear resistance under heavy loads. PTFE bushings typically offer lower friction but with reduced load capacity. POM maintains better dimensional stability in moist environments, while PTFE can handle wider temperature ranges. The choice depends on specific application requirements including load, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions.
3. Can boundary lubrication bushings handle high-speed applications?
Three-layer composite bushings are primarily designed for low to moderate speed applications. The maximum recommended sliding speed is 5 m/s when lubricated and 2.5 m/s in dry conditions. For high-speed applications, it’s crucial to consider the PV value (pressure × velocity) to ensure it remains within the specified limits. Exceeding these parameters can lead to premature failure due to thermal overload.
4. What are the key factors affecting the service life of these bushings?
Several critical factors influence service life:
PV value: The product of bearing pressure and sliding velocity
Operating temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate wear
Shaft surface quality: Roughness, hardness, and geometric accuracy
Environmental conditions: Presence of contaminants, moisture, and chemicals
Installation quality: Proper fit and alignment
Lubrication maintenance: Appropriate initial and periodic lubrication
5. Are these bushings suitable for oscillating movements?
Yes, composite self-lubricating bushings are particularly well-suited for oscillating movements. The POM surface layer provides excellent performance in applications with frequent starts, stops, and direction changes. Their self-lubricating properties ensure consistent performance even under these challenging conditions where maintaining continuous lubricant films is difficult.
6. What types of lubricants are recommended for initial lubrication?
Most standard greases are suitable, with some important considerations:
Lithium-based greases are commonly recommended
Avoid lubricants containing solid additives like molybdenum disulfide or graphite
Select viscosity appropriate for operating temperatures
Consider compatibility with environmental requirements
For food-grade applications, use USDA-approved lubricants
The manufacturer’s specific recommendations should always be followed
7. Can custom sizes and shapes be produced?
Absolutely. Most manufacturers offer extensive customization capabilities for metal polymer marginal lubricating bushings. This includes non-standard diameters, lengths, wall thicknesses, and special geometric features like flanges, grooves, and holes. Custom solutions are particularly valuable for OEM applications with specific design requirements.