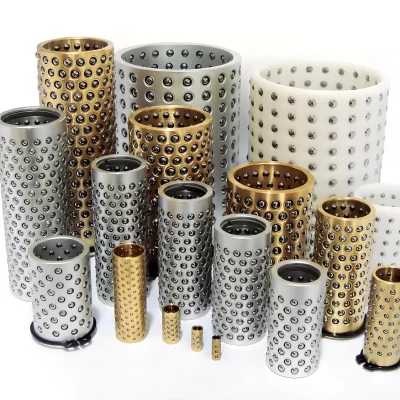
MYWAY Ball Retainer: China's Leading Manufacturer with Competitive Pricing You Can Compare
MYWAY: Expert Bushing Manufacturer in China with 20 Years of Experience.
We deliver custom & standard parts from casting to finish, IATF/ISO certified for 40+ countries.
Cost-effective solutions with reliable logistics.
Home » Ball Retainer Bearing
Ball Retainer / Ball Cage

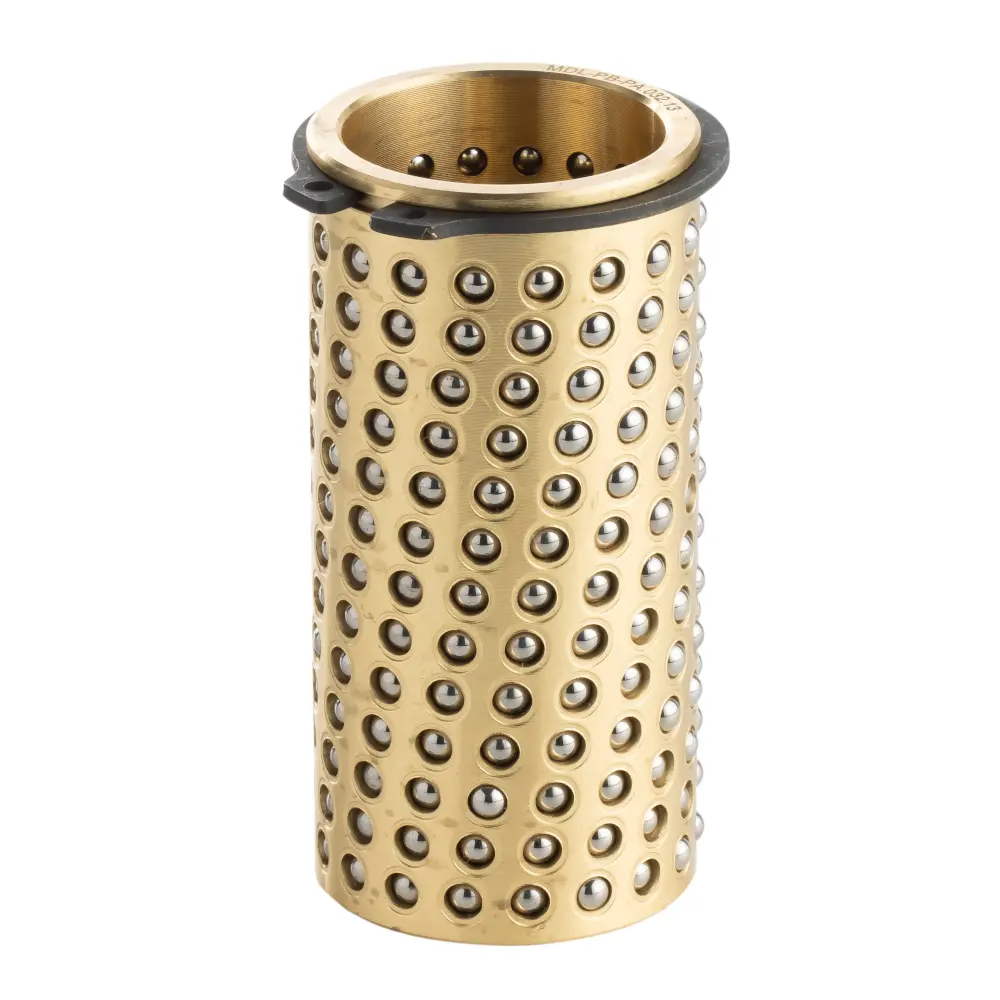
What is Ball Retainer / Ball Cage?
This ball retainer is a high-performance component engineered to replace sliding friction with precise rolling motion. It features a base material—available in copper alloy (FZH), aluminum alloy (FZL), or POM resin (FZP)—machined with an array of precision holes. Each hole is embedded with a steel ball and securely locked using a specialized circumferential oil-groove process.
The design ensures smooth, low-friction movement with high repeatability and minimal backlash. Ideal for applications requiring high precision and rigidity, it is commonly used in cold punch die sets, high-accuracy machine tools, and equipment requiring simultaneous axial and radial motion.
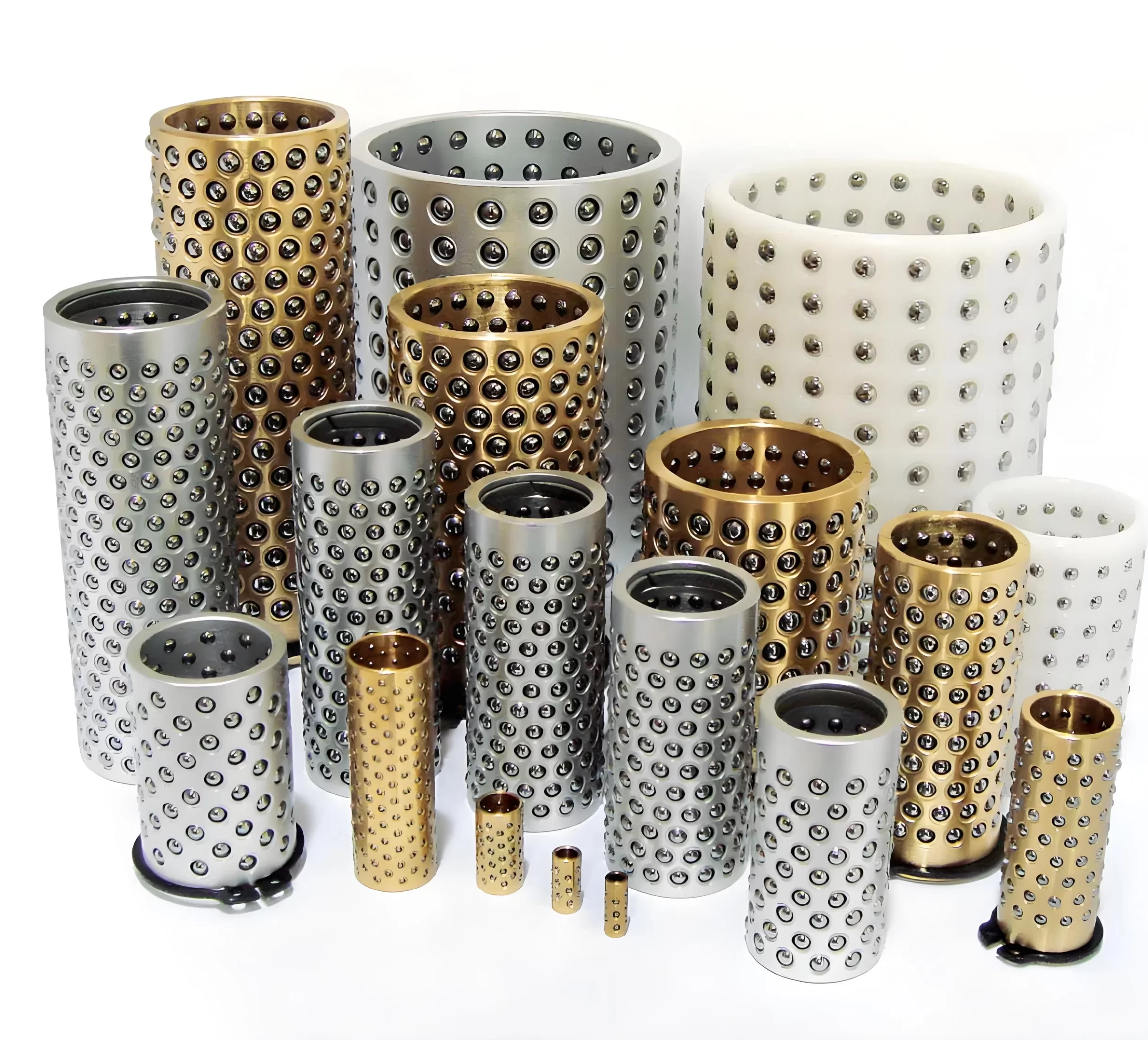
Ball Retainer / Ball Cage by Structure
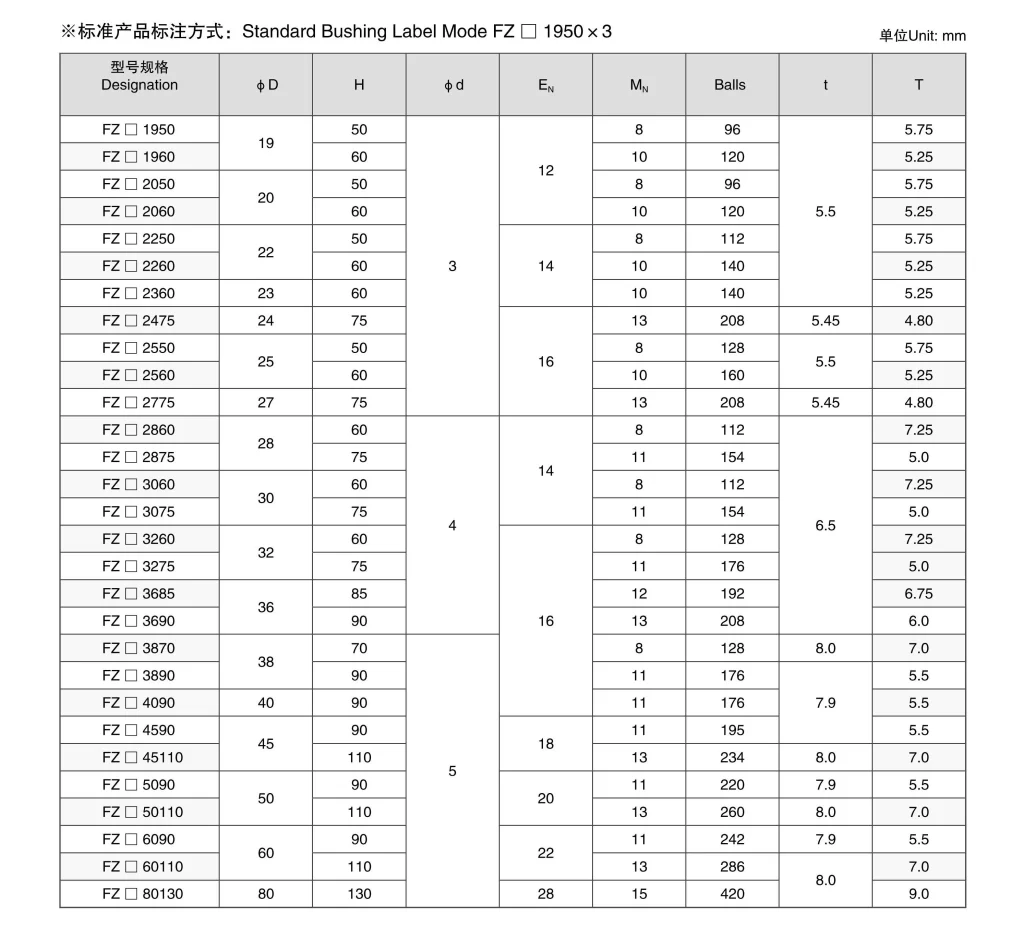
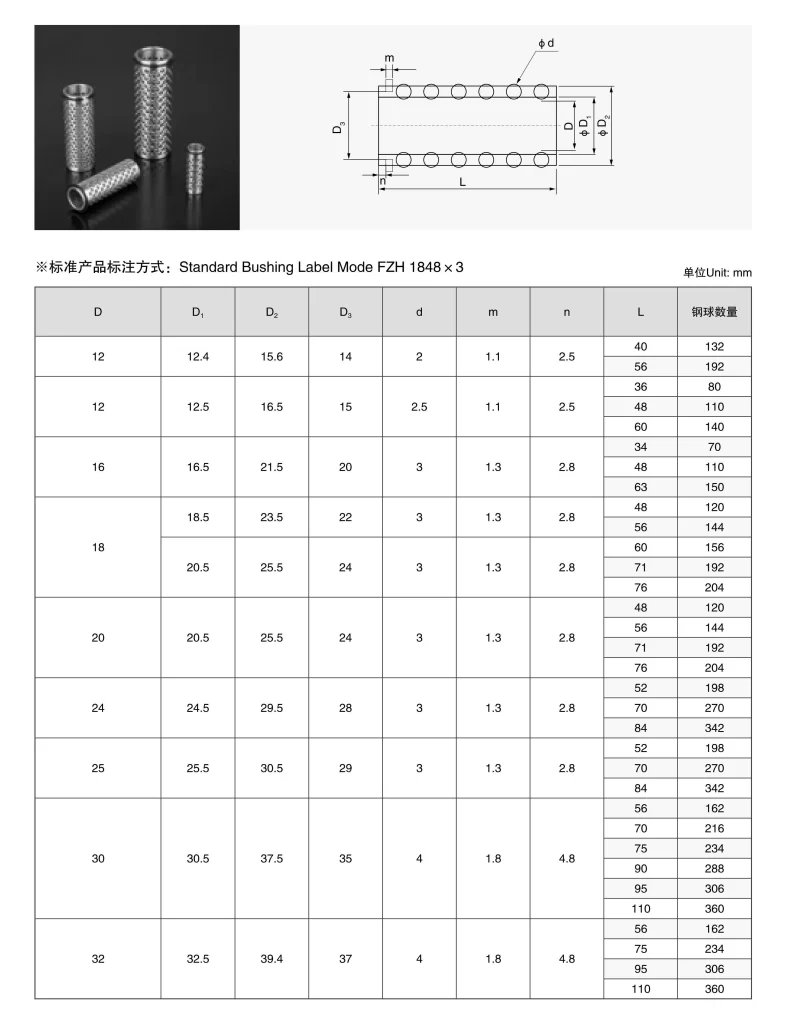
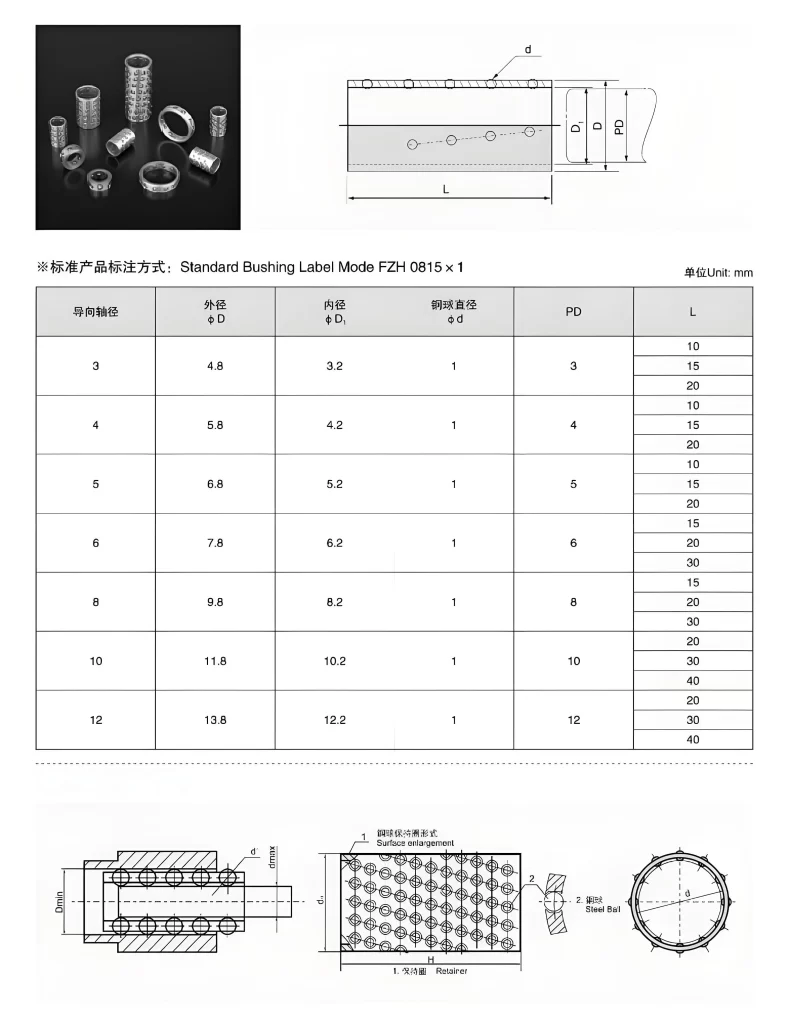
Which Specification Do You Need?
Ball Retainer / Ball Cage: The Essential Guide for Precision Engineering
In the intricate world of precision engineering, where every component must perform flawlessly under demanding conditions, ball retainers (also known as ball cages) play a surprisingly crucial role. These unassuming components are the unsung heroes within bearing systems, ensuring smooth operation, reducing friction, and extending the lifespan of machinery across countless industries. While balls and races bear the direct loads, it’s the ball retainer that manages the entire system, preventing catastrophic failure and optimizing performance. This comprehensive guide delves into the technical complexities of ball retainers, exploring their design, materials, functions, and applications to help engineers and procurement specialists make informed decisions for their mechanical systems.

Understanding Ball Retainers: More Than Just a Cage
A ball retainer is a specially designed component within a ball bearing that maintains the precise position and spacing of the balls. Think of it as the structural framework of a bearing assembly. Without this critical device, the balls would cluster together, collide, and deform under load, leading to rapid failure of the entire system. By securely housing the balls while providing ample space for rotation, ball retainers enhance the performance of rotating parts and significantly reduce friction.
These components are typically manufactured as cylindrical cages, crafted to exacting standards to ensure each ball operates independently and efficiently. Their fundamental purpose is to prevent the balls from escaping during the assembly, operation, or maintenance of bearings, making them indispensable for reliable mechanical function.
The Anatomy and Materials of Ball Retainers
The performance characteristics of a ball retainer are largely determined by its material composition. Each material offers a unique set of properties suited to specific operational environments and requirements.
Polyoxymethylene (POM) Ball Cage
Lightweight and Smooth: Usable in accelerating environments due to low mass, which reduces inertial forces.
Dry Operation Excellence: Offers outstanding performance in dry operations with smooth movement and natural lubricity.
Corrosion Resistance: Immune to rust, making it suitable for certain chemical environments.
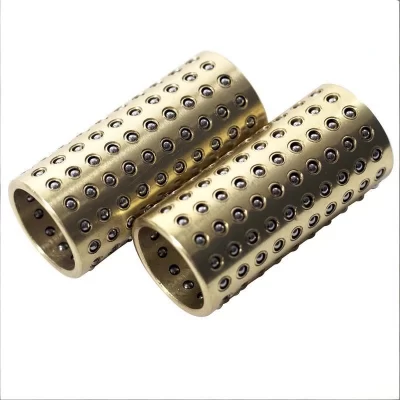
Brass Ball Cage
Universal Application: Arguably the most widely used type, combining smooth movement with a long service life.
Optimized Design: Often features a helical ball arrangement optimized for both linear and rotational movements.
Durability and Strength: Known for exceptional durability and reliability, suitable for a variety of industrial uses.
Aluminum Ball Cage
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Extremely light yet strong, ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical.
Corrosion Handling: Suitable for certain corrosive environments, often with surface treatments for enhanced protection.
Thermal Conductivity: Excellent heat dissipation properties.
Bronze Ball Cage
High Load Capacity: Ideal for heavy-duty applications and high-stress environments due to superior strength.
Wear Resistance: Excellent resistance to wear and fatigue, ensuring smooth operation and long life.
Versatility: Accommodates both radial and axial (thrust) loads in various sizes.
The balls themselves are typically made of through-hardened bearing alloy steel, ensuring high motion accuracy, flexible rolling, and a long service life. The choice of retainer material often involves trade-offs between strength, weight, friction coefficients, corrosion resistance, and cost, requiring careful consideration of the specific application.

Critical Functions and Operational Advantages
Ball retainers provide several fundamental benefits that make them essential for precision mechanical systems.
Friction Reduction and Efficiency
With minimal surface contact due to shaft and rolling friction, noise and friction damage are greatly reduced. This allows machinery to operate more efficiently with lower energy consumption and reduced heat generation.
Precise Ball Management and Load Distribution
The primary function of any ball retainer is to maintain consistent spacing between balls. This prevents clustering and ensures even distribution of loads across the bearing, preventing localized stress points that can lead to premature failure.
Enhanced Guidance and Stability
By keeping the balls on their correct path, retainers ensure stable rotational characteristics and maintain alignment within the bearing assembly. This is especially critical in high-precision applications like machine tools and medical equipment.
Heat Management
Despite a rise in temperature due to high-speed rotation, well-designed ball retainers do not lead to significant thermal issues. Certain materials, like brass and aluminum, aid in dissipating heat away from critical contact points.

Lubrication Strategies for Optimal Performance
Lubrication plays a pivotal role in the lifespan and performance of ball retainers and their associated bearings. Proper lubrication reduces internal friction and alleviates wear between parts, thereby extending component lifespan and minimizing operational noise and vibration.
Grease Lubrication
Grease remains one of the most common lubrication methods for caged bearings. Composed of oil and thickening agents, it provides a protective barrier that adheres to surfaces. When applied, the internal space of the ball retainer is filled with grease, which aids the balls in moving freely, reduces friction between bearing components, and protects against corrosion and contaminant ingress.
Fluid (Oil) Lubrication
For high-speed rotation or high-temperature environments, oil lubrication often proves more effective. Oil flows more easily between bearing components, providing better friction reduction and superior heat dissipation. This circulation helps maintain lower operating temperatures and can significantly improve bearing performance and lifespan in demanding applications.
Regardless of the method chosen, lubrication of ball retainers requires periodic maintenance. The appropriate lubricant should be selected based on environmental and operational conditions, and using the correct amount is crucial—too little leads to wear, while too much can cause churning and overheating.

Identifying and Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with proper design and lubrication, ball retainers can experience problems. Recognizing these issues early can prevent catastrophic bearing failure.
Visible Wear or Deformation: Inspect for signs of uneven wear, cracks, or permanent deformation in the cage structure.
Unusual Noise: Grinding, clicking, or rattling sounds often indicate that the retainer is failing to properly space the balls, leading to collisions.
Increased Vibration: A failing retainer can cause inconsistent rotation, manifesting as heightened vibration in the machinery.
Overheating: Excessive friction due to retainer problems often generates abnormal heat, which can be detected through thermal monitoring.
Ball Smearing or Scoring: This indicates that the retainer has allowed excessive metal-to-metal contact between components.
Regular maintenance inspections are crucial for identifying these issues before they lead to complete bearing failure. For miniature brass ball cages with compact installations, using smaller balls than standard cages, precision in inspection becomes even more critical.
Diverse Industrial Applications
Ball retainers are ubiquitous in precision engineering, finding applications across numerous industries:
High-Precision Machinery: Used in applications requiring both linear and rotational motion, such as guide parts in punching machines and mold bases.
Automotive Systems: Essential components in steering columns, transmissions, and suspension components where reliability is paramount.
Industrial Equipment: Critical for conveyor systems, pumps, and compressors that operate continuously under demanding conditions.
Aerospace and Defense: Used in control systems, actuators, and turbines where failure is not an option.
Renewable Energy: Vital components in wind turbine pitch controls and solar tracking systems that require durable, maintenance-free operation.

MYWAY: Your Trusted Partner for Precision Bushing Solutions
At MYWAY, we understand that components like ball retainers are the heart of precision motion systems. While we specialize in manufacturing top-tier sliding bearings and bushings, our engineering philosophy extends to appreciating how every component in a mechanical system interacts. Our dedication to precision manufacturing, quality materials, and technical excellence makes us the ideal partner for your most demanding application challenges.
Uncompromising Quality and Precision
Every MYWAY product reflects our commitment to excellence:
We maintain production tolerances within ±0.01 mm for consistent performance.
Our automatically controlled furnace systems ensure perfect sintering of materials.
We employ laser optical measuring instruments for regular inspections to guarantee high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish.
Comprehensive Product Range and Customization
Beyond our standard offerings, we provide extensive customization capabilities:
Self-lubricating bushings for reduced maintenance requirements.
Specialized materials including modified PTFE and copper substrates for enhanced performance.
Custom solutions tailored to your specific dimensional and performance requirements.
Global Compatibility and Expertise
MYWAY components are engineered to meet or exceed OEM specifications for a wide range of domestic and import applications. Our technical team possesses deep industry knowledge to help you select or develop the ideal solution for your specific needs, whether you’re designing new equipment or maintaining existing machinery.
Experience the MYWAY Difference
When your applications demand reliability, precision, and performance, MYWAY delivers solutions you can trust. Our extensive experience in manufacturing high-quality bushings and our understanding of precision components like ball retainers make us the smart choice for engineers and procurement specialists worldwide.
Contact MYWAY today to discuss your specific requirements, request comprehensive product information, or to request a quotation. Let us show you how our engineering expertise and manufacturing excellence can enhance your mechanical systems and contribute to your operational success.
Visit our website or speak directly with our technical sales team to discover how MYWAY precision bushings can optimize your bearing applications and drive your business forward.

MYWAY Ball Retainer / Ball Cage FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between a ball retainer and a ball cage?
In practical terms, “ball retainer” and “ball cage” are often used interchangeably to describe the component that spaces and guides the balls in a bearing. Both terms refer to the same fundamental part that prevents the balls from clustering and maintains their proper positioning.
2. How does material selection impact ball retainer performance?
Material choice directly influences friction characteristics, weight, corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and load capacity. For example, POM offers lightweight smoothness, brass provides universal durability, and aluminum excels in weight-sensitive applications, while bronze is preferred for heavy-load scenarios.
3. Can ball retainers be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers specialize in custom ball retainers. This includes modifications to material, cage design (such as helical arrangements for optimized linear and rotational movement), ball size, pocket geometry, and special coatings to meet unique operational requirements.
4. What are the consequences of improper lubrication on ball retainers?
Insufficient lubrication leads to increased friction, overheating, accelerated wear, and potential seizure. Excessive lubrication can cause fluid churning, energy loss, and overheating in high-speed applications. Contaminated lubricant introduces abrasive particles that can damage both the retainer and balls.
5. How long do ball retainers typically last?
Service life varies dramatically based on application conditions, including load, speed, temperature, alignment, lubrication quality, and environmental factors. With proper selection, installation, and maintenance, ball retainers can last the entire design life of the bearing system, often thousands of operating hours.
6. What are the signs that a ball retainer needs replacement?
Common indicators include unusual noise (grinding, clicking), increased vibration, elevated operating temperature, visible damage or wear to the cage structure, and degraded system performance. Regular maintenance inspections can identify these issues before they lead to complete failure.



