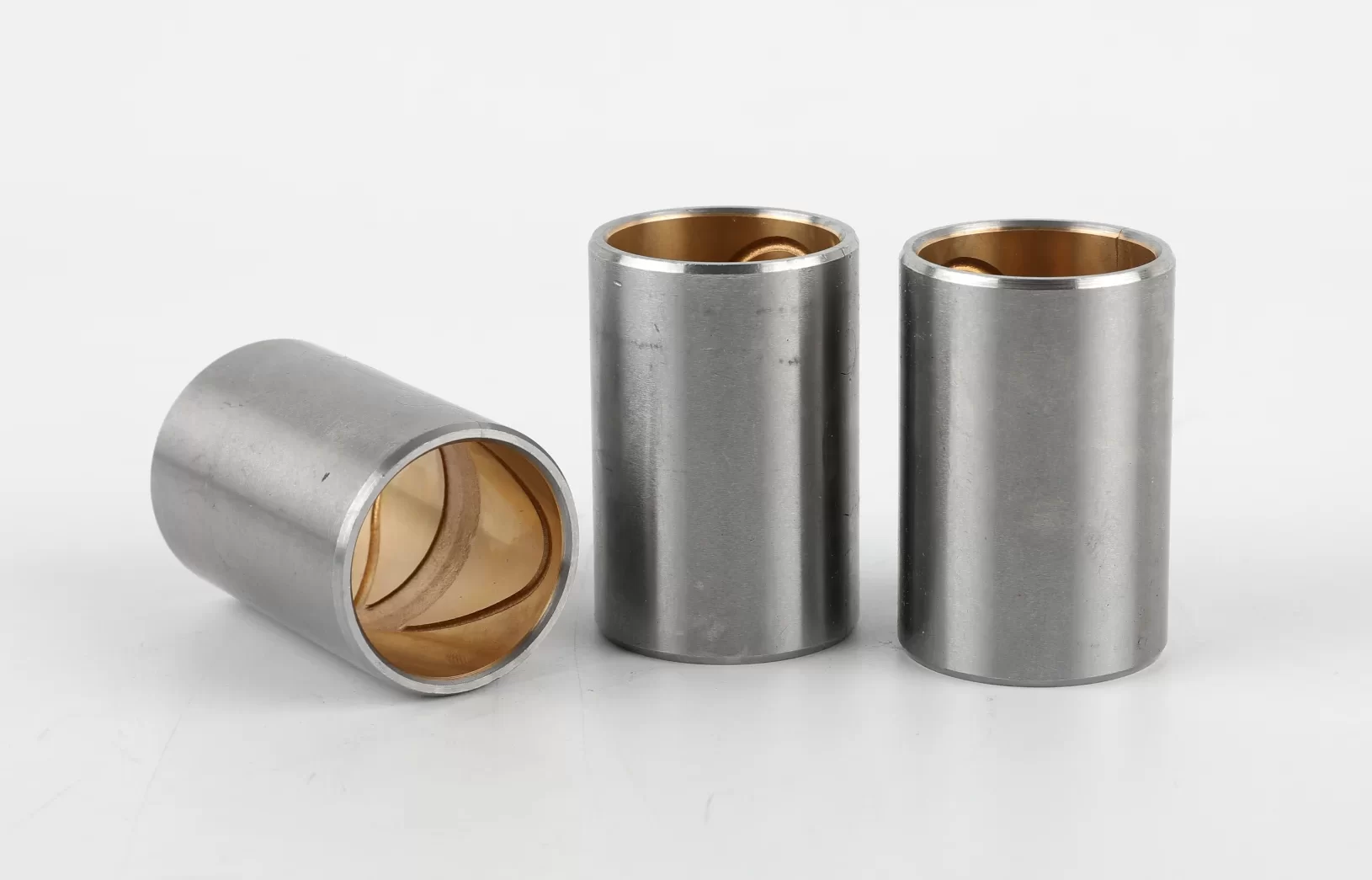
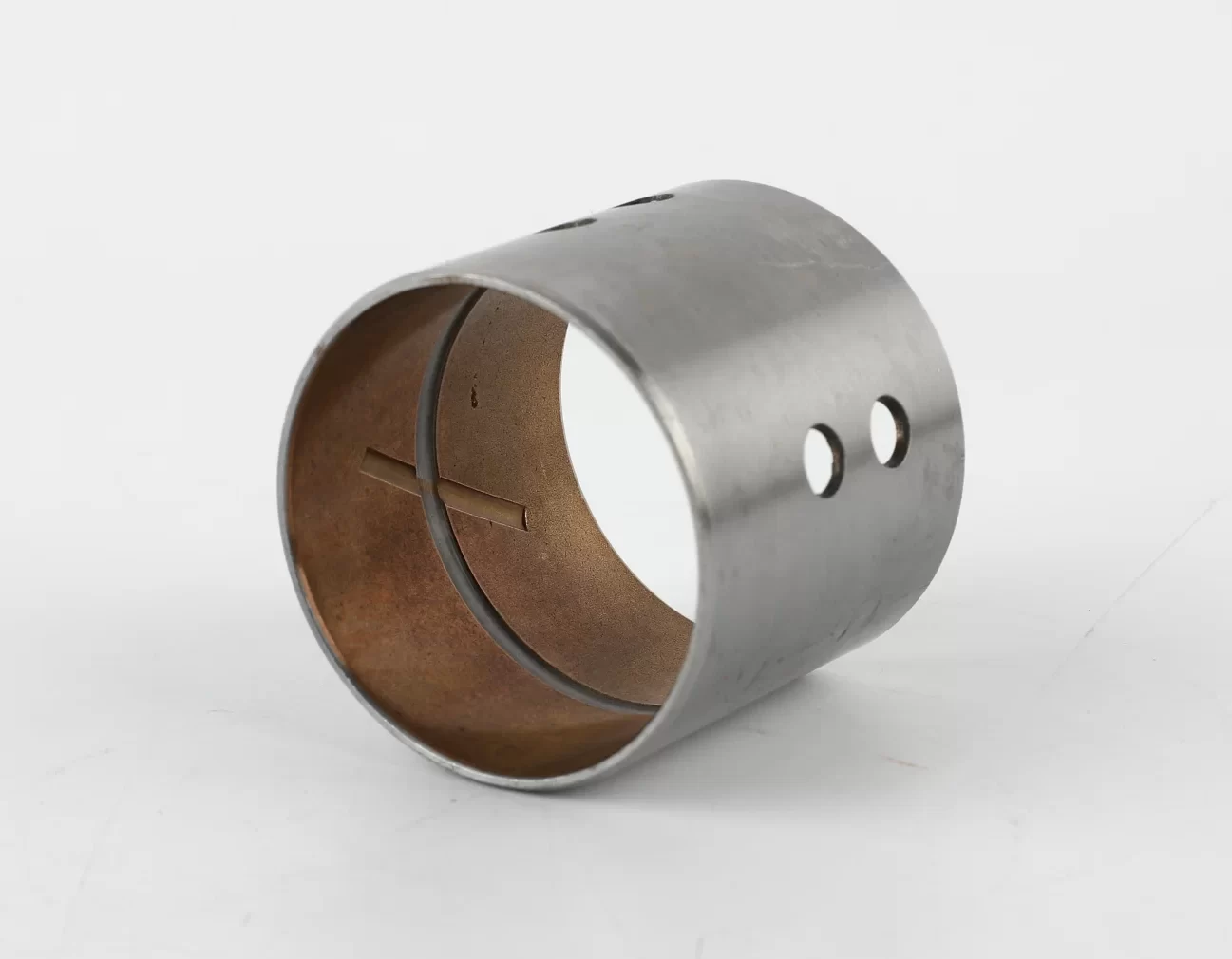
MYWAY Bimetal Bushing
Engineered for Heavy-Duty Performance & Superior Cost Efficiency
China’s Leading Manufacturer of Steel-Backed Bronze Bushings: Custom Sintered & Cast Bimetal Solutions, Unbeatable Value.
Home » Bimetal Bushing
Bimetal Bushing
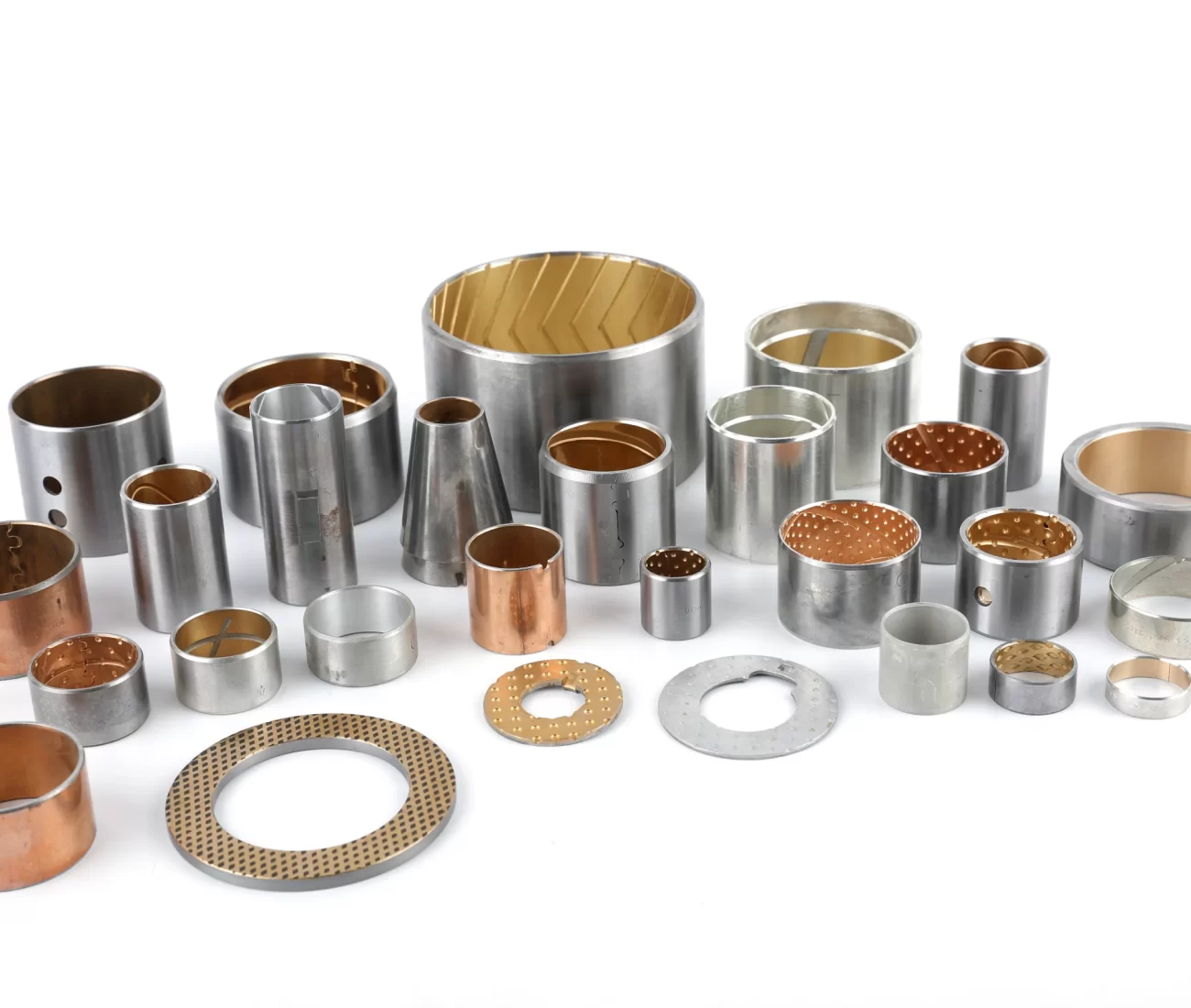

What is Bimetal Bushing?
Bimetal bearings are engineered with a high-quality low-carbon steel backing sintered or rolled with surface layers such as lead-tin bronze or aluminum-tin alloys through multi-stage processing, and are widely produced in structural forms including bushings, plain bearings, and thrust washers—among which bushings are the most common. Commonly used alloy materials include CuPb10Sn10, CuPb24Sn4, CuPb30, CuSn6Zn6Pb3, and AlSn20Cu. In alignment with growing international environmental requirements, an eco-friendly material option, CuSn6.5P0.1, has been developed and is now extensively applied in the market.
Bimetal Bushings by Structure
Bimetal Bushings by Metal Type
Bimetal Bushings by Material





Bimetal Bushings by Surface Treatment





Bimetal Bushings by Roughness
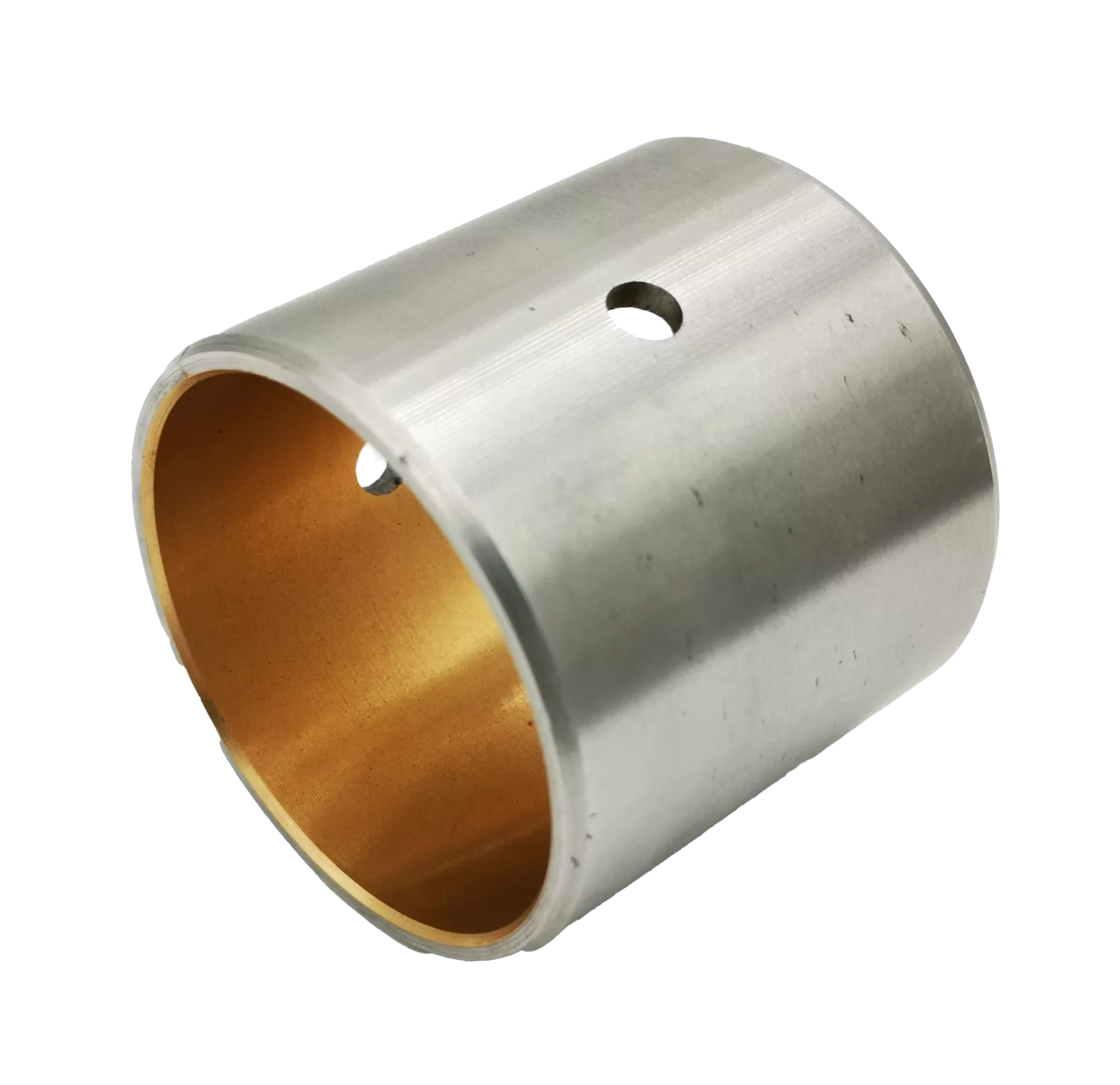


Bimetal Bushings by Shape
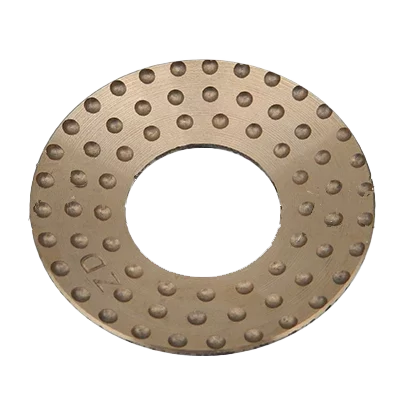
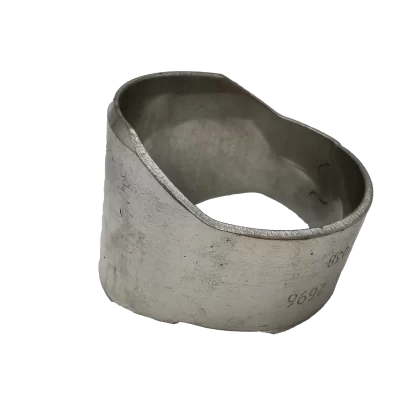
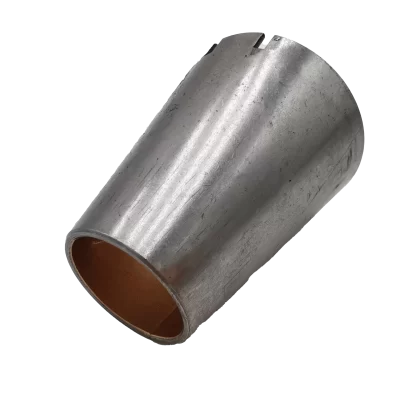



Which Specification Do You Need?
Plain Bushing
| Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. |
| 1010 | 12×10×10 | 1825 | 20×18×25 | 2620 | 30×26×20 | 3520 | 39×35×20 | 4540 | 50×45×40 | 7040 | 75×70×40 |
| 1015 | 12×10×15 | 2010 | 23×20×10 | 2625 | 30×26×25 | 3525 | 39×35×25 | 4550 | 50×45×50 | 7050 | 75×70×50 |
| 1020 | 12×10×20 | 2015 | 23×20×15 | 2630 | 30×26×30 | 3530 | 39×35×30 | 5030 | 55×50×30 | 7060 | 75×70×60 |
| 1210 | 14×12×10 | 2020 | 23×20×20 | 2815 | 32×28×15 | 3540 | 39×35×40 | 5040 | 55×50×40 | 7080 | 75×70×80 |
| 1215 | 14×12×15 | 2025 | 23×20×25 | 2820 | 32×28×20 | 3550 | 39×35×50 | 5050 | 55×50×50 | 7530 | 80×75×30 |
| 1220 | 14×12×20 | 2210 | 25×22×10 | 2825 | 32×28×25 | 3820 | 42×38×20 | 5060 | 55×50×60 | 7540 | 80×75×40 |
| 1410 | 16×14×10 | 2215 | 25×22×15 | 2830 | 32×28×30 | 3825 | 42×38×25 | 5530 | 60×55×30 | 7550 | 80×75×50 |
| 1415 | 16×14×15 | 2220 | 25×22×20 | 2840 | 32×28×40 | 3830 | 42×38×30 | 5540 | 60×55×40 | 7560 | 80×75×60 |
| 1420 | 16×14×20 | 2225 | 25×22×25 | 3015 | 34×30×15 | 3840 | 42×38×40 | 5550 | 60×55×50 | 8040 | 85×80×40 |
| 1510 | 17×15×10 | 2410 | 27×24×10 | 3020 | 34×30×20 | 3850 | 42×38×50 | 5560 | 60×55×60 | 8050 | 85×80×50 |
| 1515 | 17×15×15 | 2415 | 27×24×15 | 3025 | 34×30×25 | 4020 | 44×40×20 | 6030 | 65×60×30 | 8060 | 85×80×60 |
| 1520 | 17×15×20 | 2420 | 27×24×20 | 3030 | 34×30×30 | 4025 | 44×40×25 | 6050 | 65×60×50 | 8080 | 85×80×80 |
| 1610 | 18×16×10 | 2430 | 27×24×30 | 3040 | 34×30×40 | 4030 | 44×40×30 | 6060 | 65×60×60 | 8540 | 90×85×40 |
| 1615 | 18×16×15 | 2515 | 28×25×15 | 3215 | 36×32×15 | 4040 | 44×40×40 | 6530 | 70×65×30 | 8550 | 90×85×50 |
| 1620 | 18×16×20 | 2520 | 28×25×20 | 3220 | 36×32×20 | 4050 | 44×40×50 | 6540 | 70×65×40 | 8560 | 90×85×60 |
| 1810 | 20×18×10 | 2525 | 28×25×25 | 3225 | 36×32×25 | 4520 | 50×45×20 | 6550 | 70×65×50 | 8580 | 90×85×80 |
| 1815 | 20×18×15 | 2530 | 28×25×30 | 3230 | 36×32×30 | 4525 | 50×45×25 | 6560 | 70×65×60 | 9040 | 95×90×40 |
| 1820 | 20×18×20 | 2615 | 30×26×15 | 3240 | 36×32×40 | 4530 | 50×45×30 | 7030 | 75×70×30 | …… | …… |
Thrust Washer
| Type | Spec. | Type | Spec. |
| DP10 | 20×10×1.5 | DP26 | 44×26×1.5 |
| DP12 | 24×12×1.5 | DP28 | 48×28×1.5 |
| DP14 | 26×14×1.5 | DP32 | 54×32×1.5 |
| DP16 | 30×16×1.5 | DP36 | 62×38×1.5 |
| DP18 | 32×18×1.5 | DP42 | 66×42×1.5 |
| DP20 | 36×20×1.5 | DP48 | 74×48×2 |
| DP22 | 38×22×1.5 | DP52 | 78×52×2 |
| DP24 | 42×24×1.5 | DP62 | 90×62×2 |
MYWAY products can be tailored to your specific requirements.
Direct Replacements For
| Brand | Series/Models |
|---|---|
| GGB | AuGlide, CBM, SP, SY |
| ISB | JF800, JF720 |
| CSB | CSB820, CSB827, CSB800, CSB815 |
| DE | Bimetal |
| COB | AM |
Applications of Bimetal Bushing
Two-Metal Bushings: A Comprehensive Guide to Steel-Backed Bronze Bushings
In the world of industrial machinery and automotive engineering, bimetal bushings stand as critical components for enhancing performance and durability. Combining the strength of steel with the wear resistance of bronze, these bushings offer a cost-effective solution for a wide range of heavy-duty applications. This article delves into the types—such as Sintered Bimetal Bushing and Cast Bimetal Bushing—materials, benefits, and applications of two-metal bushings, providing valuable insights for engineers and purchasers.
What Are Bimetal Bushings?
Bimetal bushings, also known as two-metal bushings, are sliding bearings engineered from two distinct metal layers. The base typically consists of a high-quality, low-carbon steel (such as SAE 1008/1010), which provides robust structural support and impact resistance. Bonded to this steel backing is a inner layer—often a bronze alloy like CuPb10Sn10 or CuSn6Zn6Pb3—that delivers excellent wear resistance, conformability, and anti-frictional properties. This composite structure is achieved through advanced processes like sintering or centrifugal casting, creating a metallurgical bond at the interface for superior performance.
Common Materials and Manufacturing Processes
The performance of a bimetal bushing heavily depends on its material composition and manufacturing method.
Steel Backing: The base is typically low-carbon steel, chosen for its high strength and ability to withstand substantial loads and shock impacts.
Bronze Alloy Liner: Common lining materials include:
CuPb10Sn10: This leaded tin bronze offers excellent anti-seizure properties, good wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. It’s suitable for medium to high-speed applications with significant impact loads.
CuSn6Zn6Pb3: A general-purpose tin bronze used under moderate loads and sliding speeds, often found in connecting rod bushings and compressor parts.
CuPb24Sn4: Known for high fatigue strength and bearing capacity, though it can be prone to lead segregation.
Primary manufacturing methods include:
Sintered Bimetal Bushing: This powder metallurgy process involves sintering bronze alloy powder onto the steel strip at high temperatures (e.g., around 920°C). It forms a porous interface (porosity can be around 15.4%) that can be impregnated with lubricant, enhancing performance.
Cast Bimetal Bushing: Techniques like centrifugal casting are used to create a metallurgical bond between the two layers. While this method can sometimes result in higher porosity and oxidation compared to other methods, it offers good production efficiency and coating thickness.
Key Features and Performance Advantages
Steel-backed bronze bushings are renowned for their superior performance characteristics:
High Load and Impact Strength: These bushings can support high dynamic loads (up to 140 N/mm²) and are resilient against shock and vibratory loads, making them ideal for heavy machinery.
Excellent Wear Resistance and Low Friction: The bronze lining provides a low-friction surface, with a coefficient of friction typically ranging from 0.04 to 0.15 under oil or grease lubrication, reducing power loss and improving efficiency.
Wide Temperature Range: They operate effectively in temperatures up to 150°C with grease and up to 250°C with oil lubrication.
Customizability: Bushings can be designed with various lubrication features (grooves, oil holes) and are available in different types, including flange bimetal bushes for axial positioning and thrust washers.
Material and Cost Efficiency: Compared to some traditional methods like centrifugal casting, the sintered bimetal process can create a more uniform alloy layer thickness, saving material and improving cost-performance.
Typical Applications Across Industries
The versatility of bimetal bushings makes them suitable for numerous sectors:
Automotive Industry: Used in engine connecting rods, balance shaft bushings, kingpins, gearboxes, and brake systems.
Construction and Heavy Machinery: Applied in track rollers for excavators and bulldozers, support wheels, and the linkage systems of heavy equipment.
Industrial Machinery: Found in compressors, hydraulic cylinders, punching machines, conveyor systems, and various gearboxes.
Bimetal Bushings: Reliable Solutions for Demanding Applications
Bimetal bushings, known for their robust construction combining a steel backing for strength and a bronze alloy layer for superior wear resistance, serve as critical components across various heavy-duty industries. Their ability to withstand high loads, resist impact, and maintain performance in challenging conditions makes them a preferred choice for numerous applications .
Here are their primary application areas:
Construction Machinery: In heavy equipment like excavators, bulldozers, and loaders, bimetal bushings are vital for undercarriage and drive components. They are extensively used in track rollers, idler wheels, and other pivotal connections within the walking mechanisms of construction machinery, where they endure significant shock loads and abrasive conditions .
Automotive Systems: The automotive industry relies on these bushings for their durability and friction-reducing properties. Key applications include engine connecting rods, piston pin bearings, balance shaft bushings, and various chassis components such as balance bridges and leaf spring seats . They perform reliably in high-stress environments, contributing to the vehicle’s longevity and performance.
Agricultural Equipment: For farming machinery like tractors and harvesters that operate in environments filled with dust and moisture, bimetal bushings offer excellent wear resistance and durability . This reduces the frequency of maintenance and ensures longer service life for equipment, which is crucial for agricultural productivity.
Industrial and Hydraulic Applications: These bushings provide dependable performance in hydraulic cylinders, compressors, and various industrial machinery . Their design, which can incorporate lubrication features like oil grooves and indentations, helps ensure smooth operation, reduce friction, and extend equipment life in high-pressure systems .
FAQs
1. How are bimetal products lubricated?
Due to the material characteristics of bimetal bearings, they must operate in an oil-lubricated environment. Depending on the application, they are typically designed for three lubrication conditions:
Low-Speed Applications: Such as automotive balance bridges, leaf springs, brake pedals, steering knuckles, punch guide plates, and bulldozer support/idler wheels. These can be designed for grease lubrication—grease is applied during assembly and replenished periodically.
Medium-Speed Applications: Including connecting rods, punching and shearing machine shafts, and conveyor wheels. These are suitable for oil cup lubrication.
High-Speed Applications: Such as gearboxes, oil pumps, cylinders, engines, and clutches. These are designed for oil-immersion lubrication.
2. What is the difference between a Sintered Bimetal Bushing and a Cast Bimetal Bushing?
A Sintered Bimetal Bushing is made by compacting and heating bronze powder on a steel backing in a furnace, creating a porous, self-lubricating structure. A Cast Bimetal Bushing typically uses centrifugal casting to metallurgically bond a molten bronze alloy to the steel, often resulting in a denser layer but sometimes with higher porosity.
3. Why choose a steel-backed bronze bushing?
Steel-backed bronze bushings offer an optimal combination of the high strength and impact resistance of steel with the excellent wear resistance, conformability, and low-friction properties of bronze. This makes them durable and reliable for high-load and high-speed applications.
4. Are bimetal bushings self-lubricating?
While not fully self-lubricating like some polymer-based bearings, sintered bronze bushings have porosity that can retain lubricant, extending lubrication intervals. However, for optimal performance and lifespan, periodic lubrication through designed oil holes or grooves is generally recommended.
5. Can I get custom-sized bimetal bushings?
Yes, many manufacturers offer extensive customization. Bushings can be produced in various standard and non-standard sizes, with custom wall thicknesses, widths, and specific lubrication feature designs like oil holes and grooves to meet unique application requirements.
6. What are the common standards for bimetal bushings?
These bushings are often manufactured to meet international standards such as DIN ISO 3547, and material grades like SAE 792, SAE 797, and JIS LBC3.