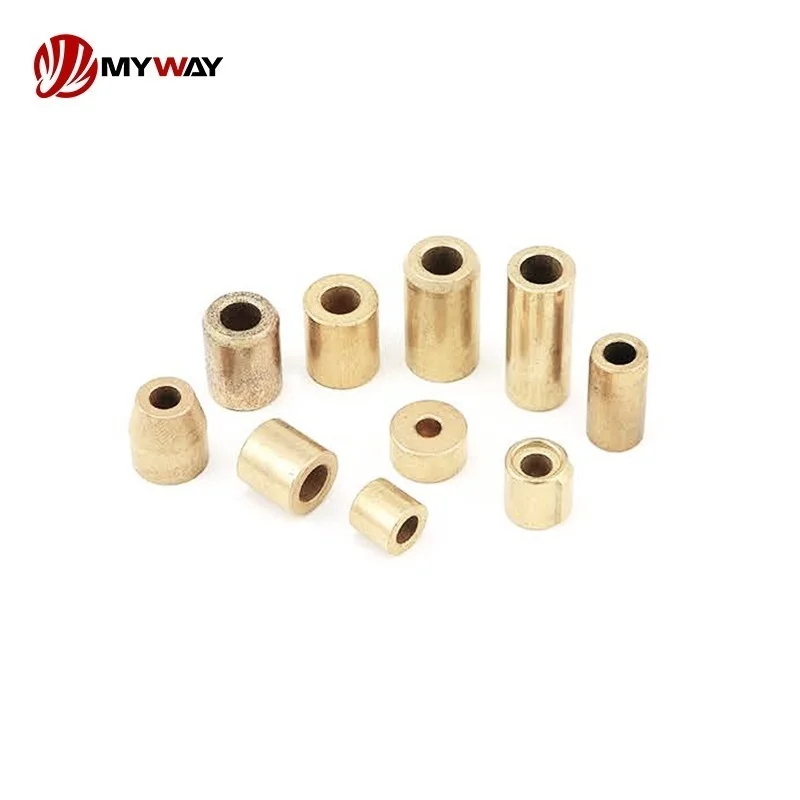
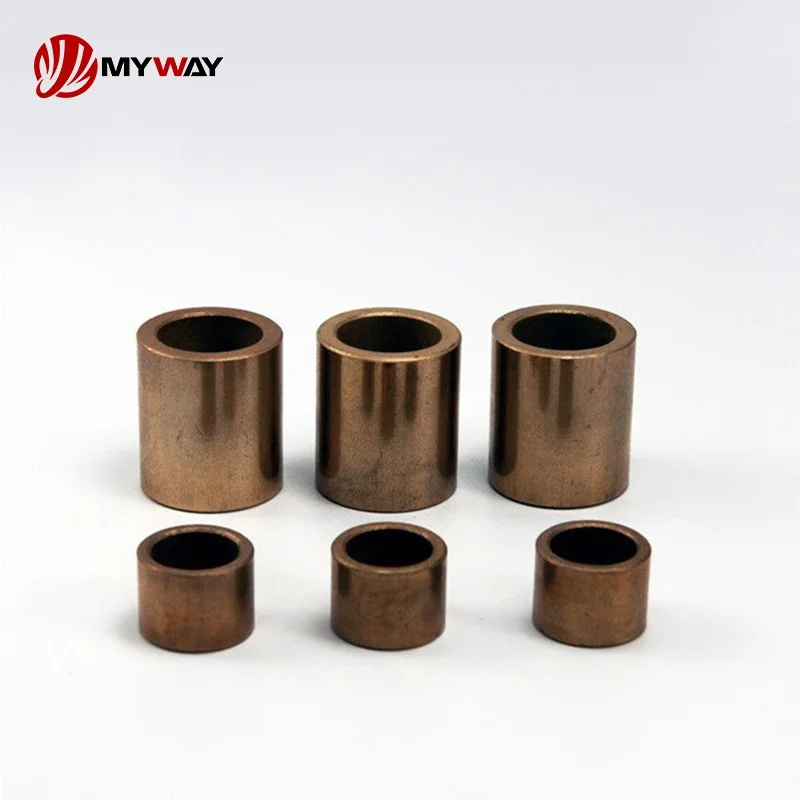
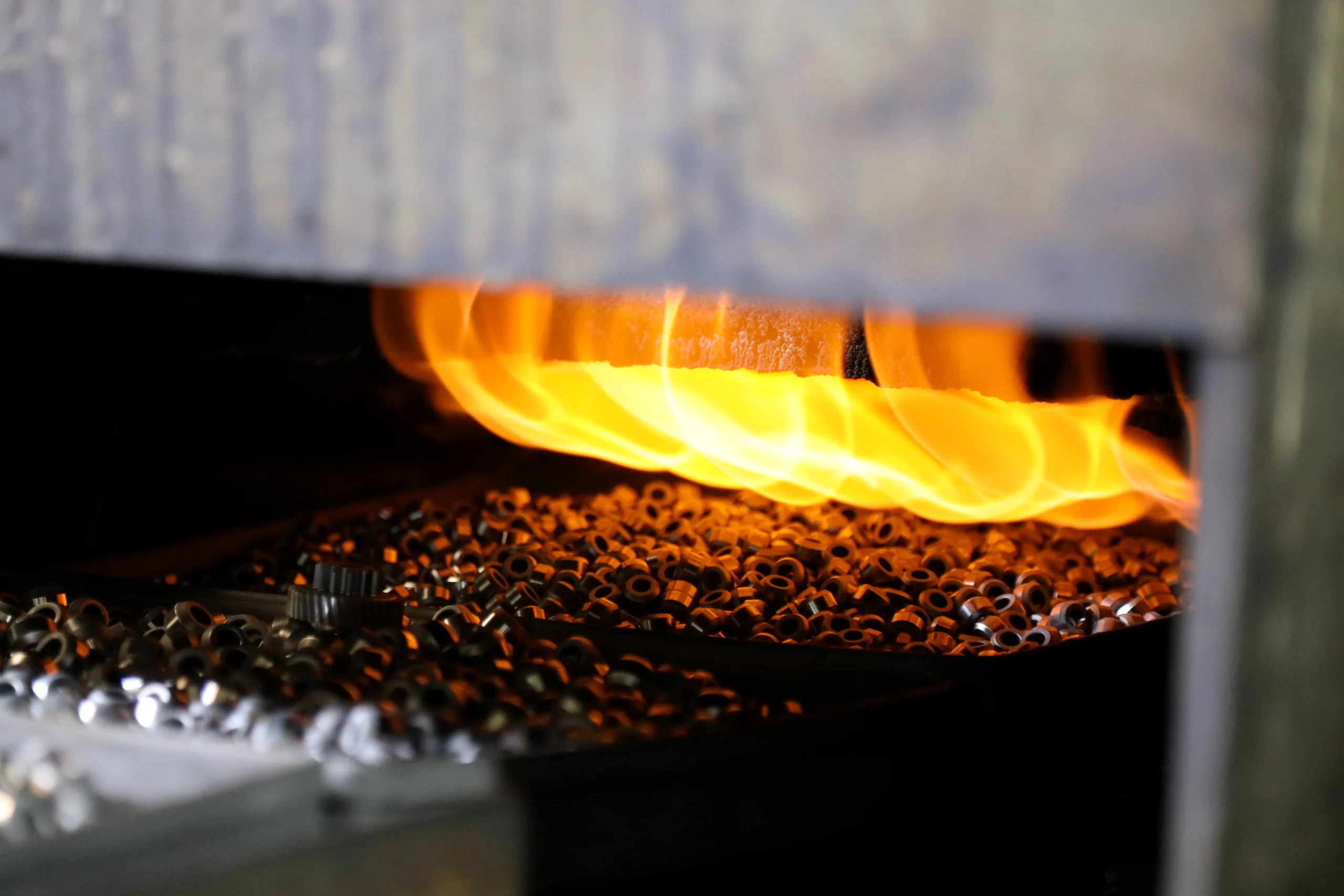
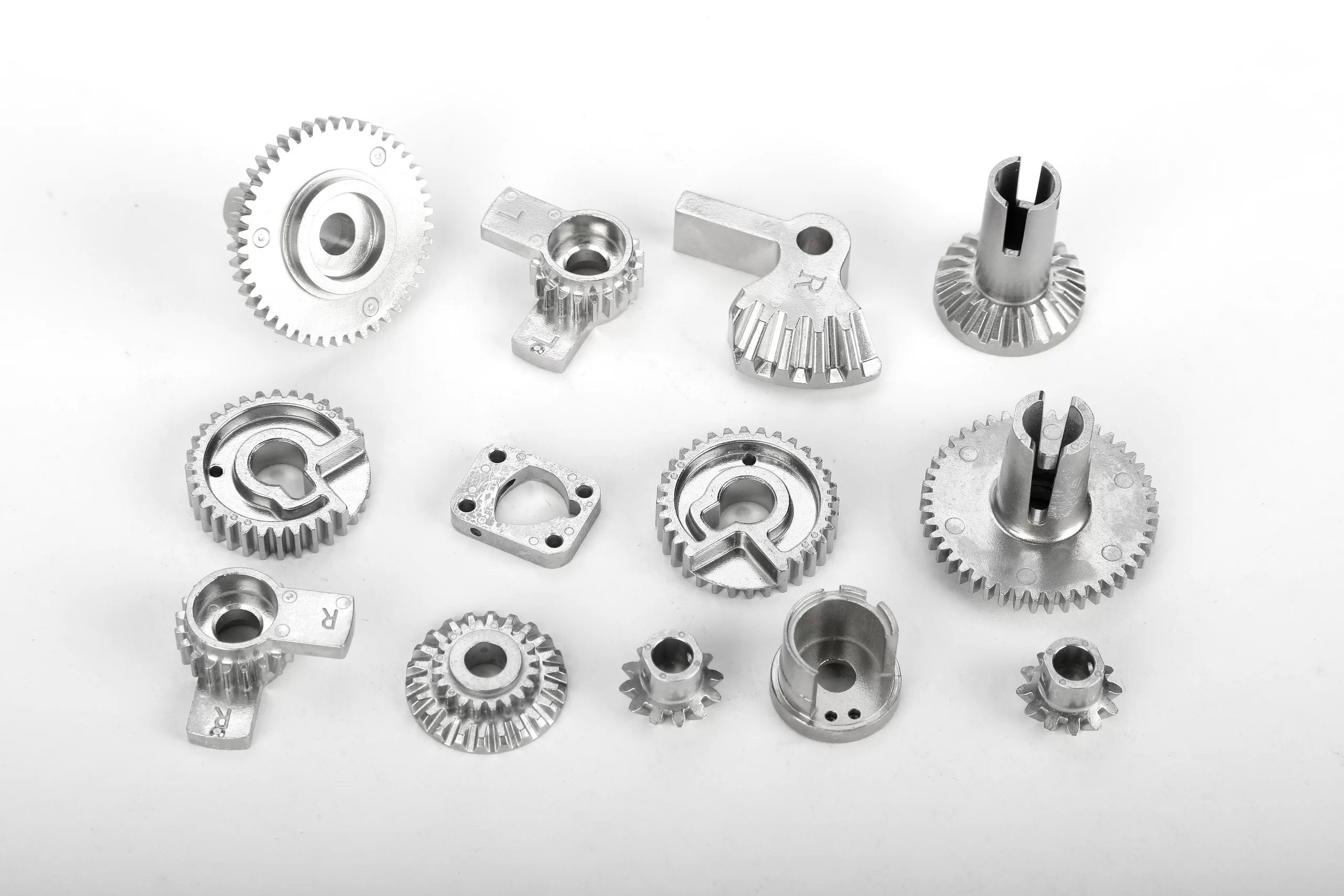
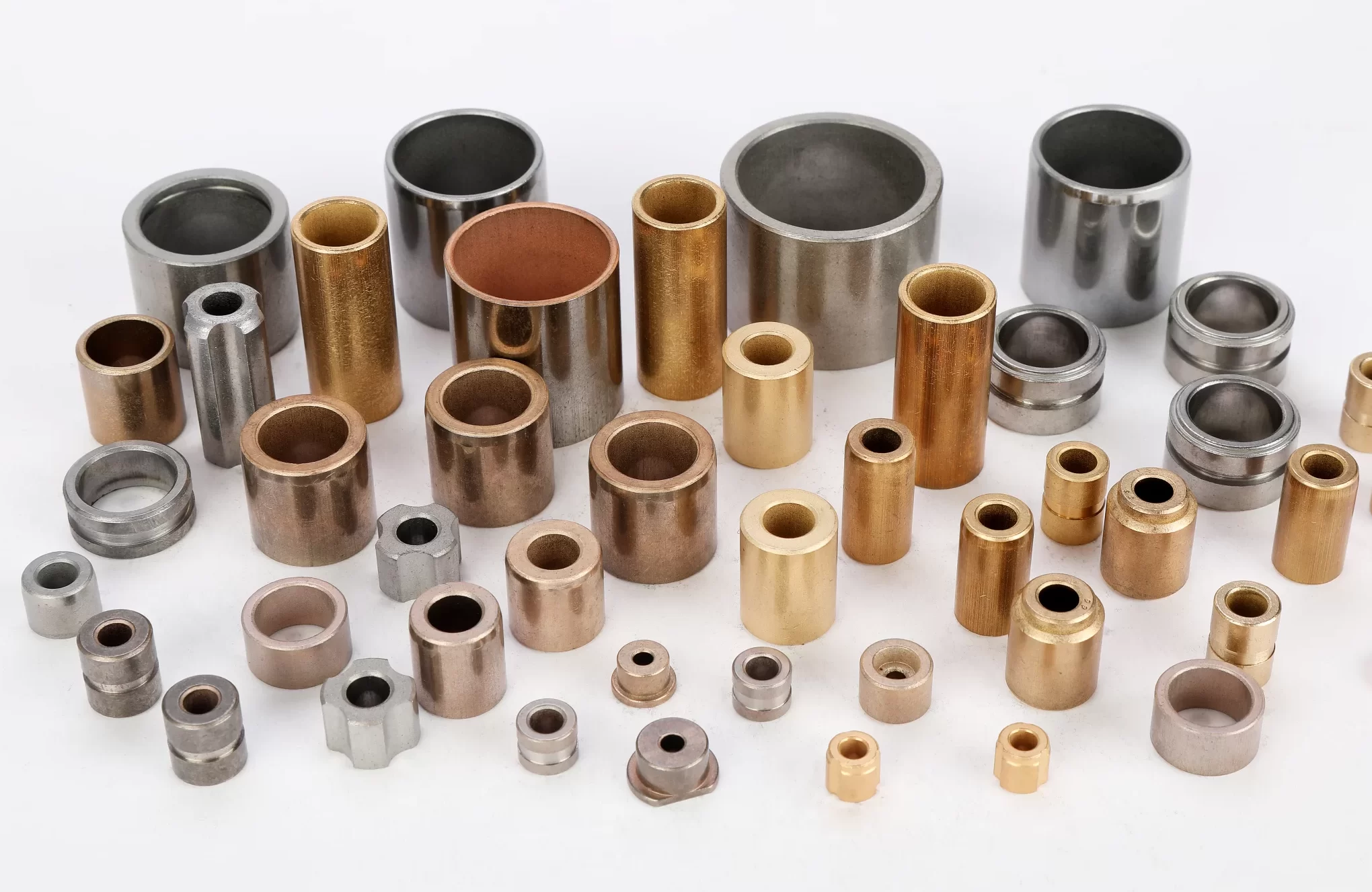
Powder metallurgy bushings provide excellent wear resistance, self-lubricating properties, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for complex shapes and applications with moderate loads and speeds.
MYWAY: Expert Bushing Manufacturer in China with 20 Years of Experience.
We deliver custom & standard parts from casting to finish, IATF/ISO certified for 40+ countries.
Cost-effective solutions with reliable logistics.
Home » Powder Metallurgy Bushing
Powder Sintered Bushing / Metallurgy Bushing

What is Powder Metallurgy Bushing / Sintered Bushing?
Sintered metal bushings are manufactured by powder metallurgy process. Copper alloy, iron based alloy or stainless steel powders are sintered at high pressure and high temperature to form uniform pore structure, then immersed in lubricating oil in vacuum environment to give the bushing self-lubricating performance and reduce downtime.
After vacuum sintering process and high pressure compaction technology, the porosity of sintered metal bushings ranges from 10% to 40%, which can achieve stable oil storage effect, ensure maintenance-free operation and long service life.
Made of all-metal material, the sintered metal bushings are characterized by rigidity, high temperature resistance and high strength. It therefore performs well against wear, corrosion and extreme conditions, making it ideal for use in automotive engines, industrial pumps, marine equipment and food processing machinery.
Sintered Bushing / Powder Metallurgy Bushings by Structure
Sintered Bushing / Powder Metallurgy Bushings by Material

Sintered Bronze Bushings
The main materials of sintered bronze bushings are CuSn10, SAE841, SINT A51, etc., which belong to tin bronze or lead bronze, and they have high strength and anti-seize performance.

Sintered Iron Bushings
Myway sintered iron bushings are made by sintering cast iron particles under high temperature and pressure, and then immersed in 18%-20% mineral oil in vacuum environment.

Oil Impregnated Bushings
The porosity of the oil immersed bushing made by powder metallurgy can be as high as 40%. Its gaps are impregnated with lubricating oil, providing long-term maintenance-free lubrication.

Sintered Steel Bushings
The most commonly used materials including stainless steel 304 and 316, which make it specifically suitable for chemical, marine, food processing and other high-corrosion applications.
Sintered Bushing / Powder Metallurgy Bushings by Type

Spherical Bronze Bushing
Spherical bronze bushings have spherical structure that distributes the load evenly, making them ideal for mechanical scenarios that require self-aligning, high load carrying and wear resistance.

Sintered Bronze Sleeve Bearing
The sintered bronze sleeve bearing has an internally connected structure and its inner and outer surfaces are smooth. Its oil content after oil immersion can reach 15% to 30%.

Sintered Bronze Flanged Bushings
Sintered bronze flanged bushings are really sleeve bearings with additional rounded flange of 3-10mm thickness, which can be axially positioned by bolts or press fit to avoid shifting.

Custom Powder Metallurgy Bushings
In addition to standard parts, Myway can also design and fabricate various special-shaped parts of powder metallurgy bushings to meet your various application requirements.
Sintered Bushing / Powder Metallurgy Bushings by Type
Which Specification Do You Need?
We offer a variety of sizes and dimensions for powder metallurgy bushings to meet different equipment requirements. Below are common product specifications:
| Parameter | Oil-Impregnated Bushing | Non-Oil Bushing |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter | 6mm – 150mm | 10mm – 200mm |
| Inner Diameter | 3mm – 130mm | 5mm – 180mm |
| Length | 5mm – 300mm | 10mm – 500mm |
| Density | 6.4 – 7.5 g/cm³ | 6.8 – 7.8 g/cm³ |
| Operating Temp | -20°C to 200°C | -40°C to 250°C |
| Tolerance | ±0.01mm | ±0.02mm |
MYWAY products can be tailored to your specific requirements.
Direct Replacements For
| Brand | Series/Models |
|---|---|
| GGB | CSM, CBM, BP25 |
| SKF | PSM |
| DAIDYNE | THERMALLOY, DAILUBO |
| PTI | BNZ, BNZF |
| ISB | FU |
| GLT | SIB-MET |
| DE | OB |
| Sankyo Oiless | SINTB |

Materials of Sintered Metal Bushings
- Copper-based Alloy: The copper-based alloys used to make sintered metal bushings are mainly tin bronze and lead bronze. The tin content of tin bronze is 5-10%, which has high wear resistance. Lead bronze is a copper-tin alloy with 5%-15% lead added to it, which can withstand impact loads.
- Iron-based Alloy: Iron-based alloys are made of pure iron or low-carbon steel powder, which are alloyed by adding copper, graphite, etc. to balance strength and self-lubricity. Its cost is 30-50% lower than that of bronze, and it is an economical medium-load solution.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel 304 or 316 has a high corrosion resistance and meets FDA standards. It is suitable for food and beverage filling equipment, medical machinery, marine machinery and other fields.
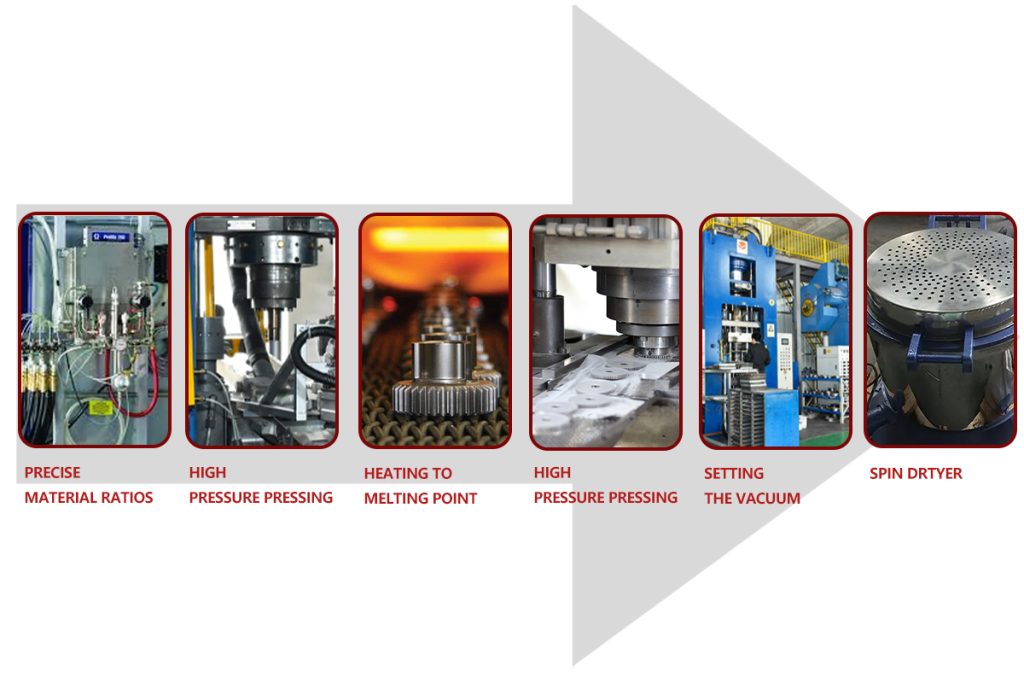
Production Process of Sintered Metal Bushings
- According to the multi-component powder dynamic proportioning system, accurate ingredients are made for different materials.
- Use special automatic forming press for powder metallurgy to press the metal powder under high pressure.
- Heat the basically formed bushing to temperature close to the melting point. The copper-based material is 700-800℃, the iron-based is 1050-1120℃, and the sintering time is 3-5 hours.
- Use a special shaping press for powder metallurgy to correct deformation and improve product accuracy.
- Put the product and oil in a container, then evacuate it to a vacuum state to allow the oil to automatically penetrate into the product.
- Put the finished bushing into the spin dryer and spin it slowly 3 times, each time for 10-20 minutes.

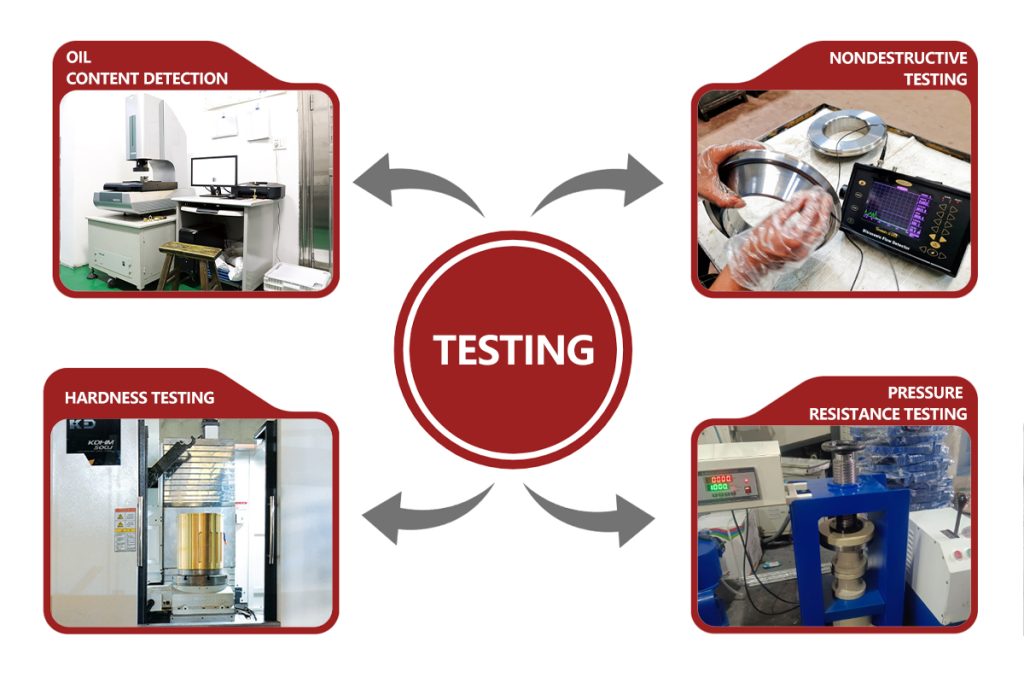
Testing of Sintered Metal Bushings
- Oil Content Detection: The oil content is calculated according to the mass difference before and after oil immersion, so as to ensure that the oil content of copper base bushings is 18-25%, and that of iron base bushings is 20-30%.
- Nondestructive Testing: Ultrasonic flaw detector is used to detect internal defects.
- Hardness Testing: Use Rockwell hardness meter, Brinell hardness meter and microhardness meter to test the hardness of quenched steel back layer, copper alloy layer and interface bonding area.
Pressure Resistance Testing: According to GB/T 6804-2008 or ISO 4379 standard, the radial compressive load is applied to the bushing by hydraulic testing machine to observe whether the bushing will crack, break or permanent deformation.
Applications of Sintered Metal Bushings
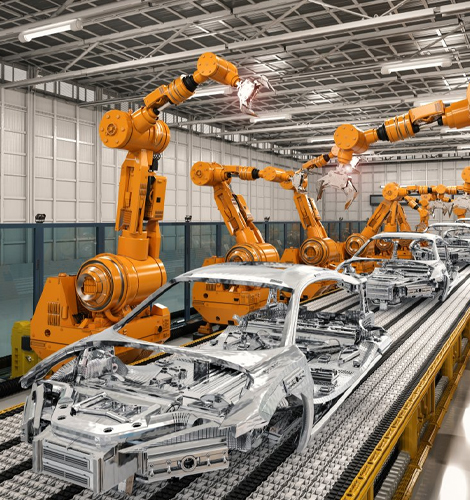

Automotive Manufacturing
Bushings are indispensable for engine system, chassis, transmission system, etc. of automobiles. They can provide stability and support for engine components, suspension systems and other key parts under high temperature and high speed.
Industrial Machinery
From electric motors to printing equipment, agricultural heavy machinery and environmental protection equipment, sintered metal bushings can withstand heavy loads, reduce friction, and reduce vibration, thereby improving equipment performance and efficiency.

Aerospace
Nickel-based bushings can withstand high temperatures of 900℃, meeting the high reliability requirements of aircraft engines. In addition, the corrosion resistance of sintered stainless steel sets enables it to maintain stable performance in humid environments.
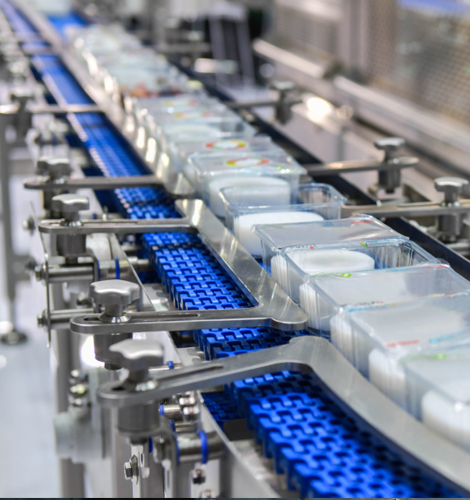

Food Processing
Myway 304/316 stainless steel bushings meet strict FDA and USDA standards, ensuring that they will not cause any pollution in food and beverage manufacturing environments, effectively reducing noise and extending maintenance cycles.
Our Factory
Sintered Bushings: The Ultimate Guide to These Self-Lubricating Workhorses
In the world of machinery, where parts spin, slide, and bear loads, few components are as humble yet vital as the Sintered Bushing. Often sold as maintenance-free and self-lubricating, these bearings are the unsung heroes inside everything from car starters and power tools to household appliances and industrial equipment.
But what exactly are they, and how do they work? This comprehensive guide will delve into the science, benefits, limitations, and applications of Powder Metallurgy Bushings.
What Are Sintered Bushings?
A Sintered Bushing, also known as a Sintered Bronze Bushing or Porous Bronze Bushing, is a type of plain bearing manufactured through a process called powder metallurgy. Unlike bearings machined from a solid metal bar, they are formed from metal powder—typically bronze (a copper-tin alloy) or iron—that is pressed and heated to create a solid, yet porous, component.
The magic lies in this porosity. After manufacturing, the Oil-Impregnated Sintered Bushing is vacuum-filled with lubricating oil, which is stored within its microscopic pores. This design makes it a truly Self-Lubricating Sintered Bushing, capable of providing long-term lubrication without external grease points.
How Do Sintered Bushings Work? The Self-Lubricating Magic
The operating principle of a PM Bushing is elegant in its simplicity:
At Rest: At room temperature, most of the lubricating oil is retained within the bushing’s porous matrix.
In Operation: As the shaft rotates within the bushing, friction generates heat.
Oil Release: This heat causes the impregnated oil to expand and slowly seep out from the pores onto the bearing surface.
Lubricating Wedge: At higher speeds, this released oil can form a thin lubricating film or “wedge” that separates the shaft from the bushing, minimizing metal-on-metal contact and reducing wear.
Re-absorption: When the machinery stops and cools down, capillary action draws most of the oil back into the pores, ready for the next cycle.
This built-in lubrication system is what makes the Sintered Bronze Bearing so popular for applications where maintenance is difficult or impossible.
The Powder Metallurgy Manufacturing Process
The creation of a Powder Metallurgy Sintered Bearing is a multi-step process that ensures its unique properties:
Compacting: Metal powder is fed into a precision die and pressed under high pressure into the desired shape (a “green” part).
Sintering: The “green” part is heated in a controlled atmosphere furnace to a temperature just below the metal’s melting point. This fuses the powder particles, creating a solid, porous structure with significant strength.
Sizing (Optional): For critical tolerances, the sintered part may be pressed again to calibrate its final dimensions.
Oil Impregnation: The bushing is placed in a bath of lubricating oil under a vacuum. The vacuum removes air from the pores, allowing the oil to fully saturate the component, resulting in a ready-to-use Oil Impregnated Bearing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sintered Bronze Bushings
Advantages:
Maintenance-Free Operation: The primary advantage. No need for external re-lubrication, reducing downtime and cost.
Cost-Effective: The powder metallurgy process is highly efficient for mass production, making Sintered Bronze Bushings very economical.
Suitable for High Speeds: Their design allows them to perform well in high-speed rotational applications.
Good Load Capacity: They can support relatively high radial loads.
Shock & Vibration Damping: The porous structure can help absorb vibrations and reduce noise.
Long Service Life: When applied correctly, they offer excellent durability.
Disadvantages:
Limited Low-Speed Performance: The self-lubricating effect relies on frictional heat. In very slow or intermittent motion, insufficient oil may be released, leading to higher wear.
Sensitivity to Edge Loading: They perform best under evenly distributed loads. Misalignment can cause premature failure.
Temperature Limitations: Extreme temperatures can cause the oil to degrade or evaporate.
Requires a Hard Shaft: For optimal life, they should run against a hard, smooth, and precision-ground shaft.
Potential for Contamination: In dusty environments, abrasive particles can clog the pores and impair lubrication.
Common Applications of Sintered Bushings
Thanks to their unique blend of features, Sintered Bronze Bearings are found in a vast array of industries:
Automotive: Starter motors, window regulators, wiper systems, and pumps.
Household Appliances: Washing machines, fans, blenders, and power tools.
Industrial Machinery: Conveyors, printing equipment, packaging machines, and agricultural equipment.
Office Equipment: Printers and copiers.
Conclusion
Sintered Bushings are a brilliant engineering solution, offering a maintenance-free, cost-effective, and reliable bearing option for countless applications. Understanding their working principle, advantages, and limitations is key to selecting the right bearing for your needs. Whether you’re designing a new product or maintaining existing equipment, the self-lubricating performance of a Powder Metallurgy Bushing often provides an unbeatable balance of performance and value.
MYWAY Powder Metallurgy Bushing FAQs
1. How do Oil Impregnated Bushings Work?
Our sintered metal bushings have uniform pore structure with porosity of up to 40%, which effectively locks in lubricating oil. When the bushing is in operation, the heat and movement release oil to the surface, achieving lifelong self-lubrication without external maintenance.
2. What is The Design Process for Custom Powder Metallurgy Bushings?
- Requirement Analysis:determine whether the load type is radial or axial, ambient temperature, medium and other parameters;
- Material Selection:recommend bronze (heavy load), iron-based (economical) or stainless steel (corrosion resistant) according to your needs;
- Simulation Verification:simulate stress distribution through finite element analysis (FEA) to optimize porosity and structure;
- Prototype Test:we can provide 5-50 samples, and the test cycle is 2-4 weeks;
- Mass Production:our minimum order quantity is 200 pieces, and the automated production line supports fast delivery.
Note: complex special-shaped parts (such as asymmetric spherical surfaces) require additional 3D printing molds, and the delivery time will be extended by 1-2 weeks.
3. Do Powder Metallurgy Bushings Require Regular Maintenance?
The self-lubricating design of sintered metal bushings can achieve long-term maintenance-free, but the maintenance cycle needs to be adjusted according to the working conditions.
4. What Factors Affect the Service Life of Powder Metallurgy Bushings?
- Overload Risk:Exceeding the rated load will cause pore collapse and shorten the service life by more than 50%;
- Lubrication Failure:Long-term high temperature (> 250℃) will cause carbonization of the lubricating oil, and high-temperature grease needs to be selected;
- Pollution Intrusion:When used in a dusty environment, you need to seal it to prevent wear.
Regular cleaning and selection of surface coatings can extend the service life by 2-3 times.
5. What are sintered bronze bushes?
Sintered bronze bushes are self-lubricating plain bearings made from bronze powder. The powder is pressed and sintered to form a porous structure, which is then impregnated with oil. This allows them to lubricate themselves during operation without needing external maintenance.
6. How long do sintered bushings last?
The service life of a PM Bushing depends on many factors, including load, speed, operating temperature, alignment, and shaft hardness. Under correct operating conditions, they can last for the entire life of the machine.
7. Can sintered bushings be re-lubricated?
While they are designed to be maintenance-free, some larger Sintered Bushings can be re-lubricated through oil holes if they begin to dry out. However, for most standard sizes, they are considered a replaceable component.
8. What are the alternatives to sintered bronze bushings?
Common alternatives include:
Polymer Bushings: Made from engineered plastics, they are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and work well at low speeds.
Metal-Polymer Composite Bushings: These feature a steel backing with a sintered bronze layer infused with a PTFE-based liner, offering very low friction and high load capacity.





















