Recent Posts
Thrust Washers: The Ultimate Guide to Axial Load Management
Introduction: The Unsung Heroes of Rotating Machinery
In the complex world of mechanical engineering, thrust washers play a critical yet often overlooked role in ensuring machinery longevity and performance. These flat, disc-shaped components serve as essential elements in managing axial loads and reducing friction across countless industrial applications. From automotive transmissions to aerospace systems, thrust washers provide the crucial interface that prevents catastrophic equipment failure while maintaining precise axial alignment.

Table of Contents
1. What is a Thrust Washer?
A thrust washer, also known as a thrust bearing washer or thrust plate, is specifically engineered to handle axial loads—forces applied parallel to a shaft’s axis. Unlike radial bearings that support rotating shafts, thrust washers prevent components from moving sideways along the shaft, ensuring they maintain proper axial positioning.
2. Key Functions and Operational Principles
Primary Functions:
Manage axial loads in rotating assemblies
Reduce friction between moving components
Maintain axial alignment of mechanical parts
Prevent metal-to-metal contact between surfaces
Absorb shock and vibration in axial direction
How Thrust Washers Work:
Thrust washers operate by creating a low-friction interface between rotating and stationary components. When axial pressure is applied, the washer surface acts as a sacrificial layer, allowing smooth rotation or oscillation while minimizing wear on both the shaft and housing. This fundamental principle makes thrust washers indispensable for rotational system health.
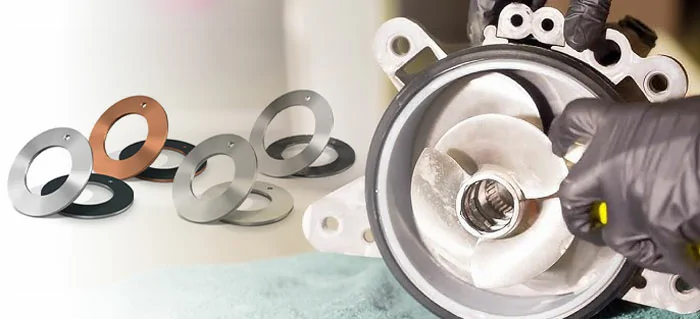
3. Common Materials and Types of Thrust Washers
The performance of a thrust washer is heavily dependent on its material, chosen based on the application’s load, speed, and environmental conditions.
Excellent wear resistance and thermal conductivity
Good compatibility with various lubricants
Ideal for general industrial applications
Available in sintered and cast variations
High-strength steel backing for structural support
Polymer or bronze sinter surface for low friction
Superior durability in heavy-load applications
PTFE/Composite Thrust Washers:
Maintenance-free operation with dry-running capabilities
Excellent chemical resistance
Self-lubricating properties
Ideal for applications where lubrication is challenging
Sintered Bronze Thrust Washers:
Fiber-reinforced composites for specific applications
Custom formulations for extreme conditions
Enhanced wear resistance and load capacity
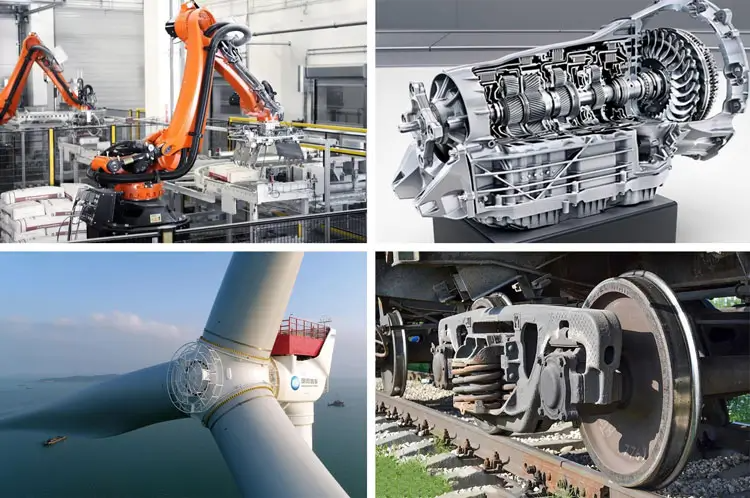
4. Key Applications of Thrust Washers
The thrust washer application spectrum is vast, covering nearly every sector of industry. You will find a machine thrust washer critical in:
Automotive Sector
Transmission systems managing gear axial pressure
Engine components requiring precise axial positioning
Steering mechanisms ensuring proper alignment
Heavy Equipment and Construction
Gearboxes in mining and construction machinery
Pivot points in heavy-duty equipment
Extreme load applications requiring durability
Aerospace and Defense
Flight control systems demanding precision
Landing gear assemblies requiring reliability
Critical systems where failure is not an option
Industrial Applications
Pumps and compressors ensuring impeller positioning
Marine propulsion systems resisting axial forces
Manufacturing equipment requiring precise alignment

5. Materials and Manufacturing Technologies
Thrust washers and bearings often work together to support and guide rotating or moving components. Specifically:

- Complementary Functions: Bearings mainly support radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft), such as deep groove ball or roller bearings. Thrust washers, on the other hand, handle axial loads (along the shaft), preventing parts from shifting due to thrust.
- Part of a Thrust Bearing Assembly: In some designs, thrust washers are part of the thrust bearing structure. For example, in thrust ball or roller bearings, washers serve as raceways for rolling elements, supporting and guiding axial movement.
- Alternative Use: In low-speed, light-load, or simpler systems, thrust washers can replace thrust bearings to reduce costs and simplify the design.
- Adjacent Installation: In industrial equipment, thrust washers are often placed next to bearings or between the inner and outer bearing rings to provide spacing, support, and axial displacement control.
6. How are thrust washers different from flat washers?
While they may look similar, thrust washers are far more advanced in both function and design:
| Comparison Item | Thrust Washer | Flat Washer |
| Main Function | Absorbs axial loads, reduces friction, limits axial movement | Distributes bolt pressure, protects surfaces, increases fastener contact area |
| Load Direction | Mainly axial (along the shaft) | Typically doesn’t bear load, static use only |
| Application Scenarios | Rotating shafts, gearboxes, transmissions, pumps with axial movement or thrust | Bolt-fastened structures like flanges or bracket mounts |
| Subject to Friction | Yes, used between moving parts; must resist friction | No, generally placed between stationary parts |
| Material Requirements | Wear-resistant, low-friction, high-strength materials like bronze alloys, steel, PTFE composites | Common materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, rubber |
7. Thrust Washers vs. Bearings
While both components manage movement and loads, they serve complementary roles:
Bearings primarily handle radial loads (perpendicular to shaft)
Thrust washers specialize in axial load management
In many systems, they work together to provide complete rotational support
8. Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper Installation Procedures
Surface Preparation: Ensure contact surfaces are clean and free of contaminants
Dimensional Verification: Confirm proper tolerances before installation
Orientation Check: Verify correct positioning (especially for grooved designs)
Press-Fit Techniques: Use appropriate tools for installation
Alignment Verification: Confirm proper seating and alignment
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection for wear patterns
Lubrication maintenance (for non-self-lubricating types)
Monitoring operating temperatures
Periodic alignment checks
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Removing Stuck Thrust Washers
Use specialized bearing pullers or extraction tools
Apply controlled heat if necessary
Employ hydraulic or mechanical presses
For severely damaged units, careful cutting may be required
Identifying Failure Symptoms
Increased axial play
Unusual noise during operation
Elevated operating temperatures
Visible wear or damage
At MYWAY, we understand that thrust washer performance directly impacts overall system reliability. Our engineering expertise delivers:
Custom Design Capabilities
Application-specific material selection
Custom dimensions and configurations
Specialized surface treatments
Prototype development and testing
Quality Assurance
Rigorous material certification
Precision manufacturing processes
Comprehensive performance testing
Consistent quality control standards
Technical Support
Application engineering consultation
Failure analysis and troubleshooting
Custom solution development
Ongoing technical support
10. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a thrust washer?
A: A thrust washer is a precision bearing component designed specifically to handle axial loads—forces parallel to a shaft’s axis. It prevents mechanical components from moving sideways while reducing friction and wear.
Q: How do I remove a stuck thrust washer?
A: Use specialized bearing pullers, apply controlled heat, or employ hydraulic presses. For severely stuck washers, careful cutting with rotary tools may be necessary while preserving the housing integrity.
Q: What does a thrust washer do in practical terms?
A: It maintains axial positioning of rotating components, manages axial loads, reduces friction between surfaces, and prevents wear on expensive machinery components.
Q: Where are thrust washers commonly used?
A: They’re essential in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, aerospace systems, marine propulsion, and any application with significant axial loads.
Q: What’s the purpose of a thrust washer in a washing machine?
A: In washing machines, thrust washers manage axial loads from the rotating drum, prevent lateral movement, and reduce wear on the main bearing assembly.
Q: How does a propeller thrust washer function?
A: In marine applications, propeller thrust washers transfer axial thrust from the propeller to the hull structure while allowing smooth rotation and preventing shaft damage.
Industry Insights and Future Trends
The thrust washer industry continues evolving with advancements in:
Material Science: New composites and surface treatments
Manufacturing Technologies: Precision engineering techniques
Design Optimization: Computational modeling for performance prediction
Sustainability: Environmentally friendly materials and processes
11. Conclusion: Partnering for Performance
Thrust washers may be small components, but their impact on mechanical system performance is enormous. At MYWAY, we combine engineering excellence with practical solutions to deliver thrust washers that meet your most demanding requirements.
Whether you need standard bronze thrust washers or custom-engineered solutions, our technical team stands ready to provide the expertise and quality you need for optimal performance and reliability.
Ready to Solve Your Axial Load Challenges?
Contact MYWAY today for expert consultation and custom thrust washer solutions tailored to your specific application requirements.
10000+ Types of Thrust Washers – Contact Us for Details