Recent Posts
The Complete Technical Guide to Bronze Worm Wheels: Materials, Performance, and Selection
1. Understanding Worm Gear Systems
Worm gear systems represent one of the most effective solutions for power transmission between non-intersecting shafts, typically at 90-degree angles. These systems consist of two primary components: the worm (a screw-like gear) and the worm wheel (a toothed wheel that meshes with the worm). What makes worm gears particularly valuable is their ability to achieve high reduction ratios in a single compact stage – often ranging from 5:1 to as much as 300:1 .
The unique operating principle of worm gears involves primarily sliding contact between the worm threads and the wheel teeth, unlike the rolling contact dominant in other gear types . This sliding action, while responsible for the system’s smooth and quiet operation, also generates significant friction and heat, making material selection critical for performance and longevity.
One of the defining characteristics of worm gears is their potential for self-locking – the worm can drive the wheel, but the wheel cannot back-drive the worm under certain conditions . This irreversible feature provides inherent braking capability, making worm gears ideal for applications like elevators, hoists, and positioning systems where safety and stability are paramount.
Table of Contents
1. Why Bronze Reigns Supreme for Worm Wheels
The historical preference for bronze worm wheels paired with hardened steel worms isn’t accidental but stems from fundamental tribological principles. The bronze-steel pairing creates an optimal combination for managing the challenging conditions within worm gear interfaces .
Tribological Advantages
Bronze exhibits exceptional compatibility with steel under sliding conditions, significantly reducing the risk of galling – a severe form of adhesive wear where surfaces weld together under pressure and sliding motion . This compatibility, combined with bronze’s natural conformability, allows the worm wheel to gradually “run-in” to match the worm’s profile more precisely over time, improving contact patterns and load distribution.
The sacrificial nature of bronze relative to hardened steel provides another strategic advantage. In cases where lubrication becomes compromised or contaminants enter the system, the softer bronze wheel will wear preferentially, protecting the more complex and costly-to-manufacture worm . This design approach recognizes that replacing a worm wheel is generally more economical than replacing both components.
Material and Performance Considerations
Bronze’s capacity to embed foreign particles represents another practical benefit. In industrial environments where contamination is inevitable, bronze’s ability to absorb small abrasive particles prevents them from circulating and causing progressive damage to both surfaces .
Despite these advantages, traditional bronze alloys do impose limitations on load-carrying capacity due to their relatively modest mechanical properties compared to steel . This constraint has driven the development of advanced bronze alloys with enhanced performance characteristics for demanding applications.
2. Bronze Alloys for Worm Wheels: A Comparative Analysis
Phosphor Bronze (Tin Bronze)
Phosphor bronze, typically containing 5-10% tin and small phosphorus additions, offers an excellent balance of strength, wear resistance, and fatigue performance. The tin content strengthens the copper matrix through solid solution hardening, while the phosphorus acts as a deoxidizer and improves fluidity during casting.
This alloy family exhibits good corrosion resistance and maintains its properties at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for various industrial environments. Its fatigue strength makes it particularly resistant to pitting and spalling under repeated loading conditions .
Nickel Aluminum Bronze (NAB)
Nickel aluminum bronze (CuAl11Ni) represents a premium category of bronze alloys offering significantly enhanced mechanical properties. The aluminum content (typically 9-12%) forms a protective aluminum oxide film that provides exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and chemical environments .
The addition of nickel and iron creates a sophisticated microstructure with hard intermetallic phases distributed throughout a tougher copper-rich matrix. This structure gives NAB alloys their characteristically high tensile strength (620+ MPa) and wear resistance . These alloys retain their mechanical properties better at elevated temperatures than tin bronzes, an important consideration in high-duty applications where heat buildup is inevitable.
Leaded Tin Bronze
Leaded tin bronzes (such as UNS C93200) contain intentional lead additions (typically 5-10%) that dramatically improve machinability and provide inherent lubricity . The lead forms dispersed, non-miscible particles within the copper matrix, creating discontinuities that facilitate chip breaking during machining operations.
While the presence of lead somewhat reduces mechanical strength, it enhances the material’s anti-seizure properties and conformability. These alloys are particularly valued for applications where boundary lubrication conditions might occur or where complex geometries require extensive machining .
Table: Comparative Properties of Common Worm Wheel Bronze Alloys
| Property | Nickel Aluminum Bronze | Phosphor Bronze | Leaded Tin Bronze |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Very High (620+ MPa) | Medium (345+ MPa) | Low (240+ MPa) |
| Yield Strength | Very High (275+ MPa) | Medium (170+ MPa) | Low (110+ MPa) |
| Hardness (Brinell) | High (170+ HB) | Medium (80+ HB) | Low (65+ HB) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Machinability | Fair to Good | Good | Excellent (70%) |
| Primary Applications | Heavy-duty, marine, high-torque | General industrial, elevated temperatures | Low-speed, boundary lubrication |
3. Failure Modes and Lubrication Requirements
Common Failure Mechanisms
Worm wheels typically fail through several identifiable mechanisms, often acting in combination rather than isolation :
Surface fatigue (pitting): Results from repeated contact stresses exceeding the material’s endurance limit, manifesting as small cavities on the tooth flanks.
Scoring: Characterized by grooves aligned with the sliding direction, caused by localized cold welding and abrasion when lubrication breaks down.
Scuffing: A severe surface deterioration where lubricant film failure leads to metal-to-metal contact and extensive material transfer.
Abrasive wear: Occurs when hard contaminants circulate between mating surfaces, particularly problematic during run-in or with unfiltered lubricants.
Spalling: Surface/subsurface fatigue resulting from repeated overloads generating shear stresses beyond the material’s yield strength.
Lubrication Strategies
Proper lubrication is arguably the single most critical factor in worm gear longevity. The challenging sliding contact conditions in worm gears create unfavorable conditions for hydrodynamic lubrication, resulting in very thin lubricant films . This necessitates lubricants with specific characteristics:
High viscosity and film strength to maintain separation under high sliding pressures
Extreme pressure (EP) additives to prevent welding under boundary lubrication
Thermal stability to resist degradation at elevated operating temperatures
Antioxidants to extend lubricant service life
The American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) provides detailed lubricant specifications for worm gearing in standard ANSI/AGMA 6134-C21, categorizing recommendations based on operating conditions, speeds, and loads .
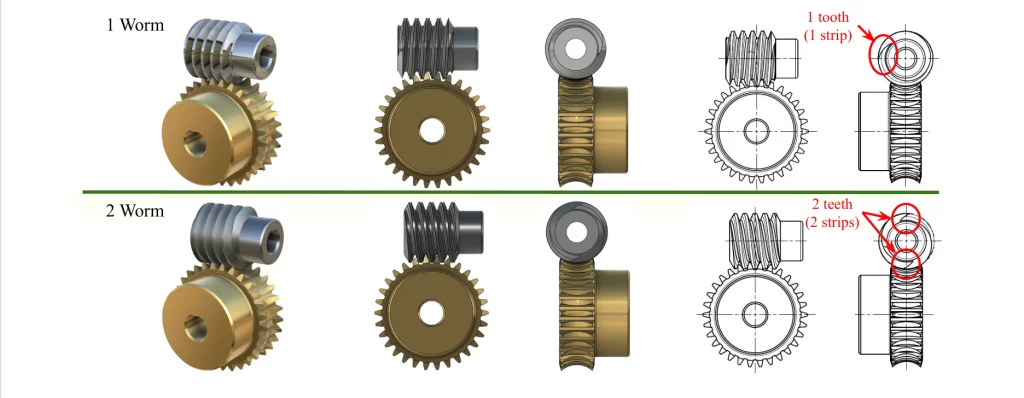
4. Selecting the Right Bronze Alloy for Your Application
Heavy-Duty and Marine Applications
For applications involving high torque, shock loads, or corrosive environments, nickel aluminum bronze typically delivers the best performance and lowest total cost of ownership. Its exceptional strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance justify its premium cost in these demanding conditions .
General Industrial Use
For most industrial applications without extreme operating conditions, phosphor bronze provides an optimal balance of performance and cost. Its good mechanical properties, wear characteristics, and fatigue strength suit it for continuous operation in environments like conveyors, machine tools, and industrial actuators.
Specialized Applications
Leaded tin bronzes find their niche in applications requiring complex geometries with extensive machining, or where marginal lubrication conditions exist. Their excellent machinability and embedded lubricity make them suitable for low-speed applications or where maintenance intervals may be extended.

While proper selection of worm wheel materials is crucial for system performance, the supporting components – particularly bronze bushings – play an equally vital role in ensuring reliability and longevity. At MYWAY, we specialize in manufacturing premium bronze bushings that complement high-performance worm gear systems.
Advanced Material Expertise
Our comprehensive range of bronze bushing solutions includes:
Self-lubricating bronze bushings with graphite plugs for maintenance-free operation
High-load capacity bushings in nickel aluminum bronze for demanding applications
Precision-machined bushings in leaded tin bronze for complex geometries
Custom alloy formulations tailored to specific operational requirements
Engineering and Manufacturing Excellence
With deep expertise in tribological systems, MYWAY engineers understand how bushing performance impacts overall gear system efficiency. Our manufacturing capabilities include:
Centrifugal casting for superior material density and consistency
5-axis CNC machining for precise geometrical accuracy
Advanced quality control ensuring dimensional compliance
Custom engineering support for application-specific solutions
Complete Technical Support
We collaborate closely with our clients to analyze application requirements and recommend optimal bushing solutions that enhance overall system performance. Our technical team provides comprehensive support from material selection through installation guidance.
Experience the MYWAY difference in your power transmission systems. Contact us today for technical consultation or to request a competitive quotation on high-performance bronze bushings tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is bronze almost universally used for worm wheels instead of steel?
Bronze’s unique combination of properties makes it ideally suited for worm wheel applications. It offers excellent compatibility with steel, reducing friction and minimizing the risk of galling. Bronze’s conformability allows it to adapt to the worm’s profile during run-in, improving contact patterns. Additionally, bronze serves as a sacrificial material – in case of lubrication failure, the less expensive wheel wears preferentially, protecting the more complex worm .
What is the typical service life of a bronze worm wheel?
Service life varies dramatically based on load conditions, operational speeds, lubrication quality, and alignment accuracy. Under proper conditions with adequate lubrication, bronze worm wheels can last 10,000+ hours. Heavy-duty applications with frequent shock loads may experience shorter lives, while optimally maintained systems in stable environments can operate significantly longer.
Can worn bronze worm wheels be repaired or must they always be replaced?
While severely damaged worm wheels typically require replacement, moderately worn wheels can sometimes be remanufactured through processes like reboring and sleeving. However, this approach depends on the extent of damage, the specific application requirements, and economic considerations. For precision applications, replacement is often recommended to ensure optimal performance.
How does nickel aluminum bronze differ from phosphor bronze in practical terms?
Nickel aluminum bronze (NAB) offers substantially higher strength, hardness, and wear resistance compared to phosphor bronze. While phosphor bronze provides adequate performance for many applications, NAB’s superior mechanical properties and exceptional corrosion resistance make it preferable for heavy-duty applications, corrosive environments, and situations where reliability is critical .
What lubrication intervals are recommended for bronze worm wheels?
Lubrication maintenance depends on operating conditions, duty cycle, and lubricant type. For continuous operation, lubricant inspection every 500 hours and annual replacement represents a typical starting point. However, manufacturers’ specific recommendations should always take precedence, as conditions vary significantly between applications. Monitoring oil condition and temperature provides the best guidance for optimal lubrication schedules.

100000+ Types of Bushings – Contact Us for Details



