Recent Posts
How Bushing Failure Triggers Costly Centrifugal Pump Wear Ring Damage
In the world of industrial fluid handling, centrifugal pumps are the relentless workhorses. Their performance is often taken for granted—until efficiency drops, energy bills soar, and unplanned downtime halts production. While worn impellers or cavitation often take the blame, a more insidious and frequently overlooked component failure is often the root cause: bushing degradation leading to catastrophic wear ring damage.
This article explores the critical link between bushing health and wear ring integrity, explaining the failure mechanism, its severe operational and financial consequences, and how a strategic upgrade to high-performance bushings can eliminate this problem.
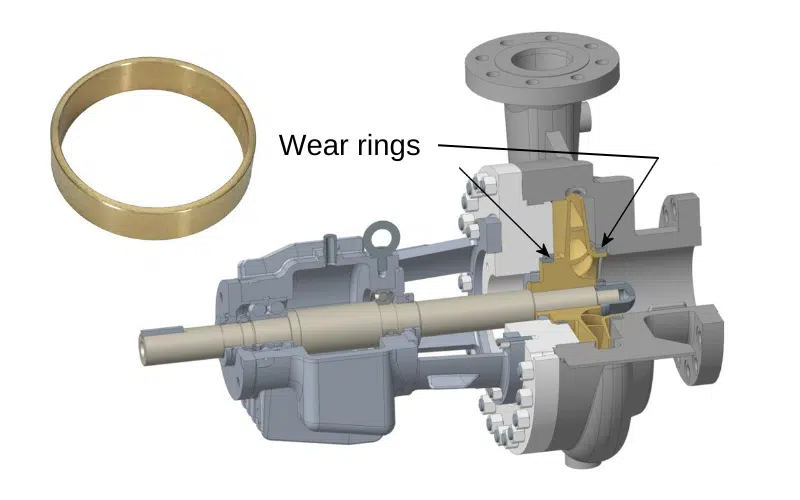
Table of Contents
1. The Precision Partnership: Bushings and Wear Rings
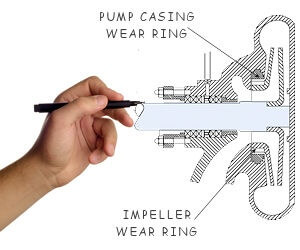
To understand the failure, one must first understand the partnership. In a centrifugal pump, wear rings (sometimes aptly called “efficiency bands”) are precision components installed on the impeller and/or casing. Their primary role is not to wear sacrificially but to maintain a minute, controlled clearance that separates high-pressure discharge fluid from low-pressure suction fluid. This seal minimizes internal recirculation (leakage), which is paramount for maintaining pump efficiency and developed head.
Bushings—including sleeve bushings, throat bushings, and interstage bushings—play a different but equally vital role. They act as bearings, supporting and centering the rotating shaft within the stationary pump casing. A key bushing, often called the throat bushing, is located near the mechanical seal. Its clearance is critical for controlling the flow and pressure of fluid entering the seal chamber.
Together, bushings and wear rings create the stable, aligned, and sealed environment necessary for optimal pump operation. The failure of one directly and rapidly compromises the other.

2. The Failure Chain Reaction: From Bushing Wear to System-Wide Damage
The degradation of a supporting bushing initiates a destructive chain reaction. Here’s the typical failure progression:
Step 1: Bushing Clearance Widen
Due to normal wear, abrasion from pumped solids, or corrosion, the internal diameter of a critical bushing (e.g., the throat bushing or a sleeve bearing) increases. This allows the pump shaft greater freedom of movement.
Step 2: Shaft Displacement and Vibration
The enlarged clearance permits excessive radial and axial shaft deflection. The once-stable rotation becomes unstable, leading to increased vibration and loss of precise shaft centering. Research confirms that increased wear ring clearance directly affects the radial balance of the pump and influences vibration intensity.
Step 3: Asymmetric Wear Ring Contact
The wobbling or misaligned shaft causes the impeller to run eccentrically. The carefully engineered uniform clearance around the wear rings is lost. The impeller wear ring begins to rub intermittently or continuously against the casing wear ring in a non-uniform pattern.
Step 4: Accelerated, Catastrophic Wear Ring Destruction
This asymmetric metal-to-metal contact leads to rapid, severe wear. The wear ring clearance, which might have been specified at 0.010 inches, can quickly double or triple. One study on a vertical centrifugal pump demonstrated that head and efficiency decrease measurably as wear ring clearance increases.
Step 5: Systemic Pump Failure
The consequences of this failure cascade are severe:
Plummeting Efficiency: With clearance widened, internal recirculation surges. The pump works harder to achieve the same output, wasting energy. The “efficiency bands” have failed.
Lost Performance: Pump capacity (flow) and head pressure drop, disrupting the entire process it serves.
Secondary Damage: Excessive vibration damages mechanical seals (leading to leaks), bearings, and can even cause fatigue cracks in the impeller or shaft.
Increased Sealing Pressure: As noted in a case study, increased throat bushing clearance can alter stuffing box pressure dynamics, making it difficult to maintain proper flush flow to a mechanical seal, accelerating its failure.
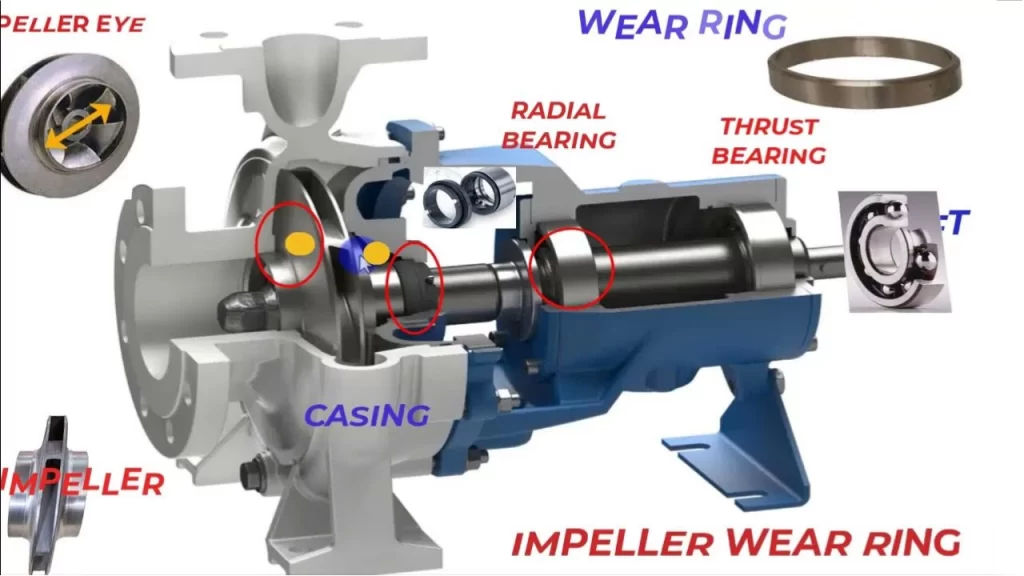
3. The True Cost: Beyond the Replacement Part
Replacing a set of wear rings is a maintenance task. However, the cost of the rings themselves is a fraction of the total business impact.
Energy Waste: A pump operating with worn wear rings can experience an efficiency loss of 10% or more, representing a continuous, silent drain on utilities.
Unplanned Downtime: The emergency shutdown to diagnose vibration, disassemble the pump, and repair multiple components halts production.
Collateral Damage: The cost of replacing failed seals, bearings, and possibly the impeller far exceeds the cost of the initial wear rings.
Labor Intensive: The repair process is complex, involving complete pump disassembly, precise measurement of clearances, and meticulous installation.

4. Breaking the Chain: The Solution is in the Source
Traditional maintenance is reactive: run until failure, then replace the worn wear rings and bushings with OEM-spec equivalents. This cycle guarantees repeat failures.
The proactive, cost-saving strategy is to break the failure chain at its source by eliminating premature bushing wear. This requires bushings engineered not just to meet specifications, but to exceed the demands of the operating environment.
Introducing MYWAY High-Performance Bushings: Engineered to Protect Your Investment
At MYWAY, we specialize in manufacturing plain bearings and bushings that are designed to withstand the conditions that cause standard components to fail. By upgrading to MYWAY bushings, you directly protect your pump’s wear rings and ensure long-term, efficient operation.
How MYWAY Bushings Solve the Problem:
Superior Wear & Abrasion Resistance: Our advanced bronze and bimetallic materials are formulated for exceptional hardness and durability against abrasive particles in the fluid stream. This translates to dramatically extended bushing life and maintained precise clearances.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: For pumps handling corrosive chemicals or seawater, we offer alloy compositions specifically designed to resist chemical attack, preventing the clearance-widening corrosion that starts the failure chain.
Optimized Lubrication & Low Friction: Our self-lubricating and oil-impregnated bushing designs ensure smooth operation even in startups or during lubrication interruptions, reducing the friction that leads to initial wear.
Custom-Engineered for Your Duty: We don’t just sell parts; we provide solutions. Our engineering team can tailor bushing material, wall thickness, lubrication grooves, and tolerances to your specific pump model, fluid, and duty cycle, ensuring an optimal fit and unparalleled performance.
5. Conclusion: Invest in Reliability, Not Just Repairs
The link between bushing failure and wear ring damage is a textbook example of how a small, inexpensive component can cause disproportionately large operational and financial losses. Moving from a reactive maintenance cycle to a proactive reliability strategy starts with specifying superior components.
Don’t let a standard bushing dictate the lifespan of your critical pump assets. By choosing MYWAY high-performance bushings, you are not just buying a part—you are investing in extended wear ring life, sustained pump efficiency, reduced vibration, and long-term operational stability.
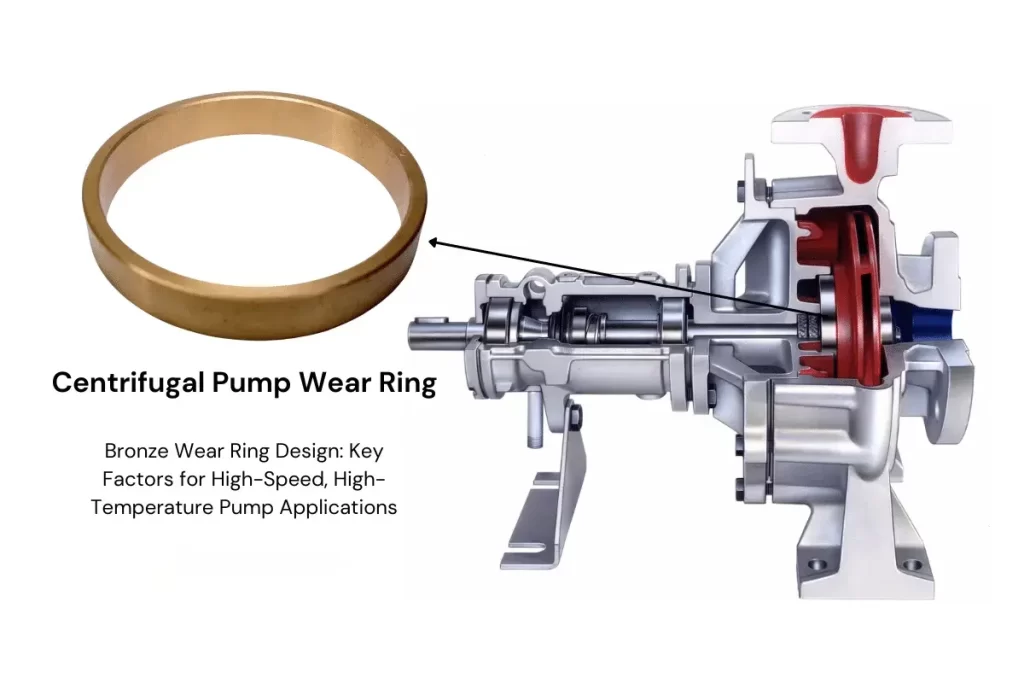
FAQ: Centrifugal Pump Bushings and Wear Rings
Q1: How can I tell if my pump bushing wear is affecting the wear rings?
Early signs include a gradual increase in pump vibration or a slow drop in flow/pressure at a constant speed. A more definitive sign is increased mechanical seal flush pressure requirements or frequent seal failures. During maintenance, always measure both bushing and wear ring clearances, comparing them to the manufacturer’s original specifications.
Q2: Should I always replace bushings when I replace wear rings?
Absolutely. If wear rings have been damaged due to excessive clearance, the supporting bushings that allowed that misalignment are also compromised. Replacing both as a set is a best practice that restores the pump to like-new internal alignment and extends the life of the entire repair.
Q3: Are non-metallic/composite bushings a good option?
In many applications, yes. Advanced composites offer excellent corrosion resistance, natural lubricity, and can tolerate dry running better than some metals. They are particularly effective in handling abrasive slurries where metallic bushings might wear quickly. The choice depends on temperature, chemical compatibility, and load.
Q4: What’s more important: the bushing material or the clearance?
They are equally critical. The wrong material will wear quickly, destroying the clearance. However, even the best material, if installed with the wrong clearance, will cause problems. Follow OEM or engineering standards (like API) for clearance, and select a material from a trusted manufacturer like MYWAY that matches your service conditions.
Q5: Can MYWAY help if I don’t have the original OEM specifications?
Yes. Our engineering team is experienced in reverse-engineering and recommending components based on pump type, shaft diameter, operating environment, and the failure history of your current parts. We help you specify not just a replacement, but an upgrade.
100000+ Types of Bushings – Contact Us for Details
