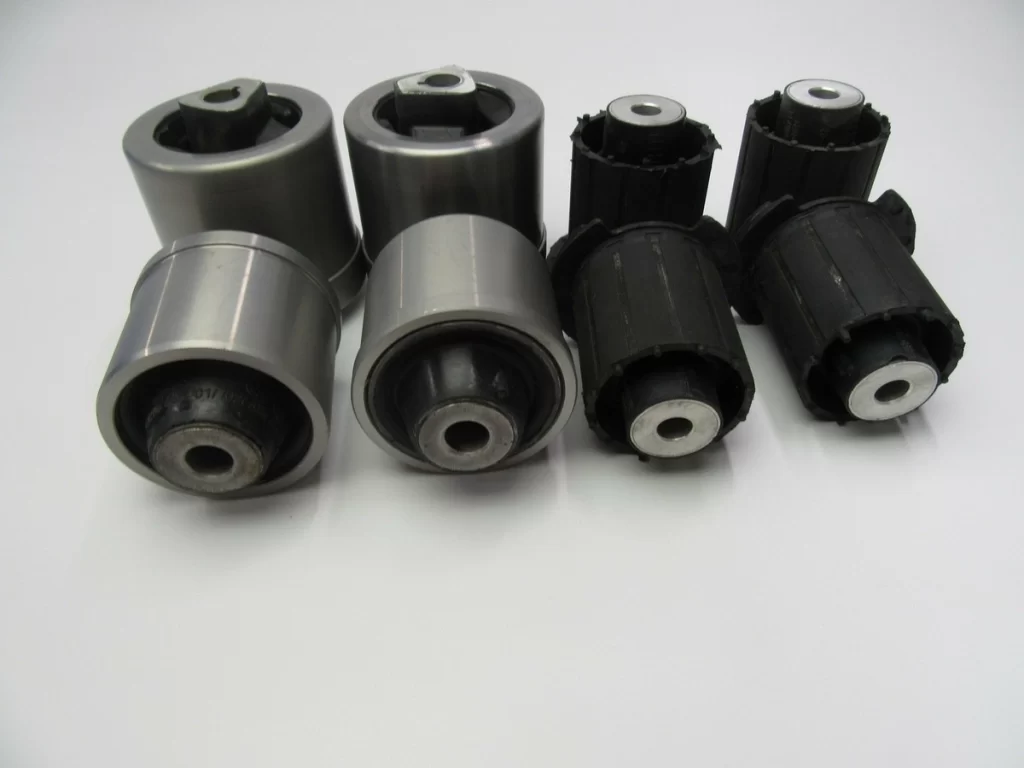
Recent Posts
Understanding Bushings and Their Critical Role in Machinery
Bushings—those unsung heroes of the mechanical world—play a fundamental role in countless applications across industries. Also known as sleeve bearings or plain bearings, bushings are sleeve-shaped components designed to reduce friction, absorb shock, and provide precise alignment between moving parts. These components serve as a protective interface between rotating or sliding components, preventing direct metal-to-metal contact and extending the equipment’s service life. From automotive suspensions to industrial machinery and power transmission systems, proper bushing installation directly impacts operational efficiency, safety standards, and maintenance costs.
The importance of correct bushing installation cannot be overstated. When properly installed, bushings ensure optimal performance, extended component life, and reduced vibration. Conversely, incorrect installation can lead to premature wear, component failure, and potentially catastrophic damage to expensive machinery. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the professional process of installing various types of bushings, with an emphasis on techniques that maximize performance and longevity.
Table: Common Bushing Types and Their Applications
| Bushing Type | Primary Materials | Typical Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Split-Taper Bushing | Steel, Bronze | Power transmission, Sprockets, Pulleys | Easy installation/removal, Accommodates various shaft sizes |
| Taper-Lock Bushing | Steel, Alloys | Conveyor systems, Industrial equipment | Secure locking mechanism, High torque transmission |
| QD Bushing | Steel | Agricultural equipment, Heavy machinery | Quick disconnect feature, Standard/reverse mount options |
| Polyurethane Bushing | Polyurethane compounds | Automotive suspension, Shock absorption | Enhanced vibration damping, Weather resistance |
| PTFE-Lined Bushing | Steel backing with PTFE layer | Food processing, Chemical applications | Self-lubricating, Corrosion resistant |

Table of Contents
1. Pre-Installation Preparation: Tools, Safety, and Inspection
1.1 Essential Tools and Equipment
Professional bushing installation requires specific tools to ensure precision and avoid damage to components. Based on industry-standard procedures, you’ll need: socket sets (typically 14mm, 17mm, 19mm), torque wrenches for accurate fastener tightening, hydraulic press or threaded press for controlled bushing insertion, rust penetrant for stubborn components, wire brush for cleaning, and appropriate safety gear including safety glasses and gloves . For specific applications such as automotive suspension work, you may also require specialized tools like spring compressors for strut assemblies .
Having the right tools before starting not only makes the process more efficient but also prevents improvisation that can lead to installation errors. For automotive applications, it’s also advisable to have jack stands for secure vehicle support, pry bars for component manipulation, and wheel chocks for added safety . The exact tool requirements may vary based on the specific application, so consult relevant service manuals for your equipment.
1.2 Safety Considerations
Safety should always be the primary concern when installing bushings. Begin with personal protective equipment (PPE): safety glasses to protect against flying debris, gloves to prevent cuts and abrasions, and steel-toed boots when working with heavy components . When working on vehicles, always use proper support systems—never rely solely on a hydraulic jack; instead, securely position the vehicle on jack stands rated for the weight .
Be mindful of stored energy in suspension systems, particularly when dealing with strut assemblies that contain compressed springs. As highlighted in Monroe’s technical guide, “Be certain the strut and spring compressor are secure and pointed away from you. Always follow the instructions provided by the spring compressor manufacturer” . Additionally, work in a well-ventilated area when using rust penetrants or lubricants, and keep your work area organized to prevent tripping hazards.
1.3 Component Inspection and Preparation
Before installing new bushings, conduct a thorough inspection of all related components. Check the shaft for scoring, corrosion, or wear that might affect bushing performance. According to technical guidelines, shaft tolerance should typically fall within f7 or h8 specifications for optimal performance . Similarly, inspect the housing bore for damage, ovalization, or contamination that could prevent proper bushing seating.
Cleaning is critical—remove all dust, dirt, paint, oil, and grease from the shaft, bushing bore, and component bore. Contamination on these surfaces will inhibit the bushing’s ability to function correctly, as bushings rely on friction and force for proper operation. Use appropriate cleaning solvents and a wire brush to achieve clean, bare metal surfaces. For automotive applications where alignment is crucial, consider marking component positions before disassembly to simplify reassembly .
2. The Professional 7-Step Bushing Installation Process
2.1 Step 1: Note the Bushing's Original Orientation
Before removal, observe that the bushing has two locations where the rubber casing connects to the outer metal ring. Use a permanent marker to clearly mark these positions on the control arm. This will serve as a reference to ensure the new bushing is installed in the correct direction.

2.2 Step 2: Remove the Bushing Using a Hydraulic Press
The most efficient method for bushing removal is with a hydraulic press. Position the bushing section of the control arm securely in the press and activate it. Listen for a distinct popping sound, indicating the bushing has loosened. Once fully dislodged, the arm will move freely.
Caution: Apply pressure gradually to avoid damaging the control arm.

2.3 Step 3: Alternative Removal with a Threaded Press
If a hydraulic press is unavailable, a threaded press (e.g., a ball joint press) can be used. Select a press cup matching the bushing’s outer diameter. Set up a driver with the same diameter as the bushing’s outer shell, and use a wrench to operate the screw-jack, pushing the bushing out of the control arm.

2.4 Step 4: Manual Removal Using a Hammer
As a last resort, strike the bushing directly with a hammer to flatten it until it can be slid out. Focus the strikes solely on the bushing to avoid damaging the control arm. Note that this method is labor-intensive and less effective.
Tip: A hydraulic press is still required for installing the new bushing, so it is advisable to wait until one is accessible.

2.5 Step 5: Clear Residual Rubber with a Socket
After removing the bushing, push out any leftover rubber using a socket that fits inside the bushing housing. If the rubber is stuck, gently separate it from the control arm edges with a flat-head screwdriver.
2.6 Step 6: Position the New Bushing in the Control Arm
Align the new bushing according to the markings made in Step 1, using the flexible sections of the bushing as a guide. Press it firmly into the control arm—it should fit snugly.
Important: Do not use lubricants to ease installation, as this may cause the bushing to slip out during operation.

2.7 Step 7: Secure the New Bushing with a Hydraulic Press
Place the control arm in the hydraulic press and activate it to seat the bushing fully. Ensure the arm remains stable during pressing to prevent misalignment of the bushing.

3. Pro Tips and Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
3.1 Professional Installation Techniques
Seasoned technicians employ several specialized techniques to ensure perfect bushing installation. For applications requiring precise alignment, use alignment sleeves or arbors to maintain accurate positioning during pressing. When installing multiple bushings in a single housing, stagger the installation to avoid creating excessive press force that could distort the housing. For particularly tight interference fits, consider cryogenic treatment of the bushing before installation—cooling the bushing can temporarily reduce its diameter for easier insertion.
Another professional approach involves thermal installation methods, where the housing is carefully heated to expand the bore slightly, creating clearance for bushing insertion. This technique is particularly useful for large bushings or when dealing with materials with different thermal expansion coefficients. However, this method requires careful temperature control to avoid compromising material properties or damaging adjacent components.
3.2 Common Installation Errors and Consequences
Even experienced technicians can make bushing installation mistakes. The most common error is misalignment during pressing, which can damage both the bushing and housing. This often results in immediate failure or significantly reduced service life. Another frequent mistake is improper lubrication—either using the wrong type or applying it to surfaces that should remain dry for proper interference fit.
Over-torquing fasteners is another prevalent issue, particularly with split-taper and QD bushings. This can cause housing distortion, bushing flange damage, or difficult removal during future service. Conversely, under-torquing can lead to loosening under operation, potentially causing catastrophic failure. Always reference manufacturer torque specifications rather than relying on instinct. Additionally, avoid the temptation to “make do” with improvised tools—using proper drivers and mandrels is essential for professional results.
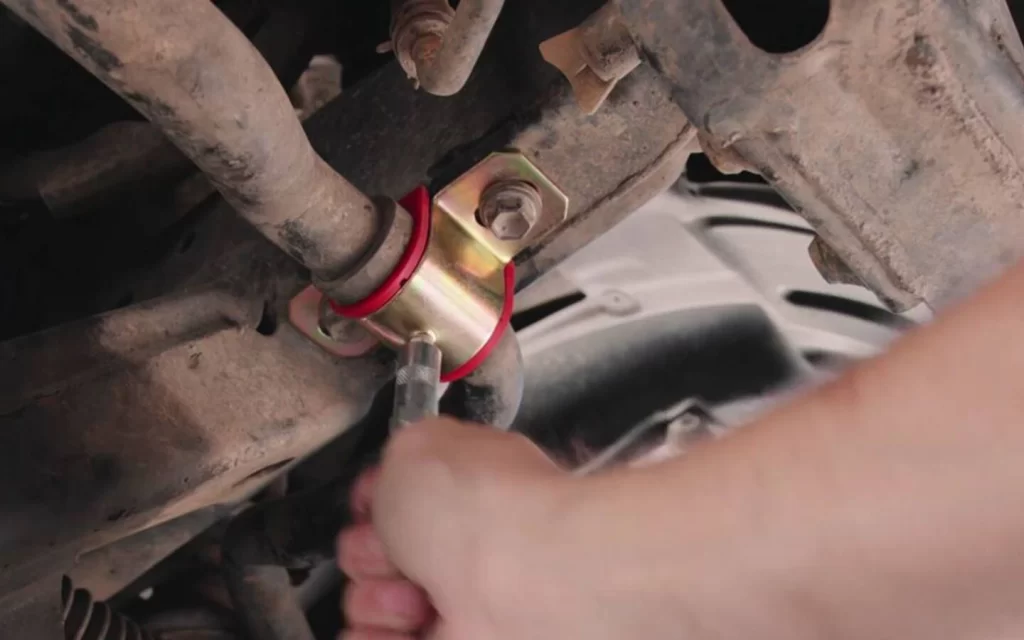

4.1 Unmatched Quality and Precision Engineering
At MYWAY, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance bushings that exceed industry standards for precision and durability. Our bushings feature advanced material formulations, including our proprietary MW-1 composite structure with a steel backing for mechanical strength, sintered bronze interlayer for enhanced heat dissipation, and a PTFE and lead mixture sliding surface that provides exceptional wear resistance and self-lubricating properties . This sophisticated material combination ensures extended service life and reliable performance in even the most demanding applications.
Every MYWAY bushing undergoes rigorous quality control throughout the manufacturing process. We utilize tungsten steel precision forming molds and maintain tight tolerances of +0.01 mm on material thickness, with regular inspections using laser optical measuring instruments . This commitment to precision ensures that our bushings install smoothly and perform consistently, batch after batch. For applications requiring exceptional corrosion resistance, we offer stainless steel variants (304 and 316) that provide outstanding performance in harsh environments.
4.2 Technical Superiority and Custom Solutions
MYWAY bushings incorporate several proprietary design features that set them apart from conventional offerings. Our innovative interface designs facilitate easier assembly while allowing the bushing to perform its elastic advantages more effectively. The optimized material structure provides superior impact absorption, protecting both the shaft and housing from damage under severe operating conditions. This technical excellence translates to tangible benefits for our customers, including reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and improved equipment performance.
Understanding that standard solutions don’t always address unique application challenges, MYWAY offers comprehensive customization options. We can tailor bushings to your specific requirements regarding dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics. Our engineering team works closely with customers to analyze application requirements and recommend the optimal bushing solution, ensuring perfect integration with your equipment.
Table: MYWAY Bushings vs. Conventional Bushings Performance Comparison
| Performance Characteristic | MYWAY Bushings | Conventional Bushings |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Static ≤ 250 N/mm², Dynamic ≤ 140 N/mm² | Typically 20-30% lower |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent (PTFE/lead sliding layer) | Varies with material |
| Corrosion Resistance | Optional stainless steel backing | Limited without special treatment |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +280°C | Often limited to -40°C to 120°C |
| Maintenance Requirements | Self-lubricating, minimal maintenance | Often require regular lubrication |
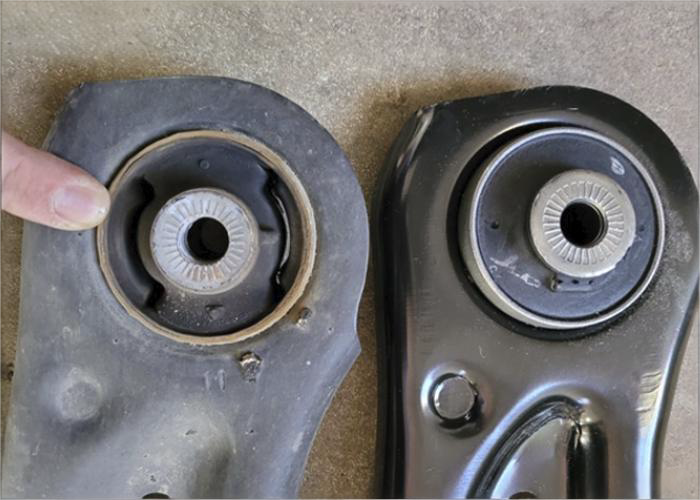

4.3 Commitment to Customer Success
MYWAY‘s dedication to customer satisfaction extends far beyond the point of sale. We offer comprehensive technical support for installation and troubleshooting, ensuring your team achieves optimal results with our products. Our global distribution network guarantees timely delivery wherever your operations are located, with flexible capacity to meet both prototype and production volume requirements. Additionally, all MYWAY bushings are manufactured in facilities compliant with international quality standards, including IATF 16949:2016 for automotive applications .
Proper bushing installation is both an art and a science, requiring technical knowledge, appropriate tools, and meticulous attention to detail. By following the professional guidelines outlined in this article, you can achieve installations that deliver optimal performance, extended service life, and reduced maintenance costs for your equipment.
When your applications demand uncompromising quality and reliability, choose MYWAY bushings. Our precision-engineered solutions, advanced material technology, and commitment to excellence make us the preferred choice for industries worldwide. Contact MYWAY today to discuss your specific requirements, request technical specifications, or place an order. Our engineering team is ready to provide the expert support you need to optimize your equipment’s performance with our high-quality bushing solutions.
Visit our website or call our technical sales team to discover the MYWAY difference in bushing technology and request your personalized quotation.
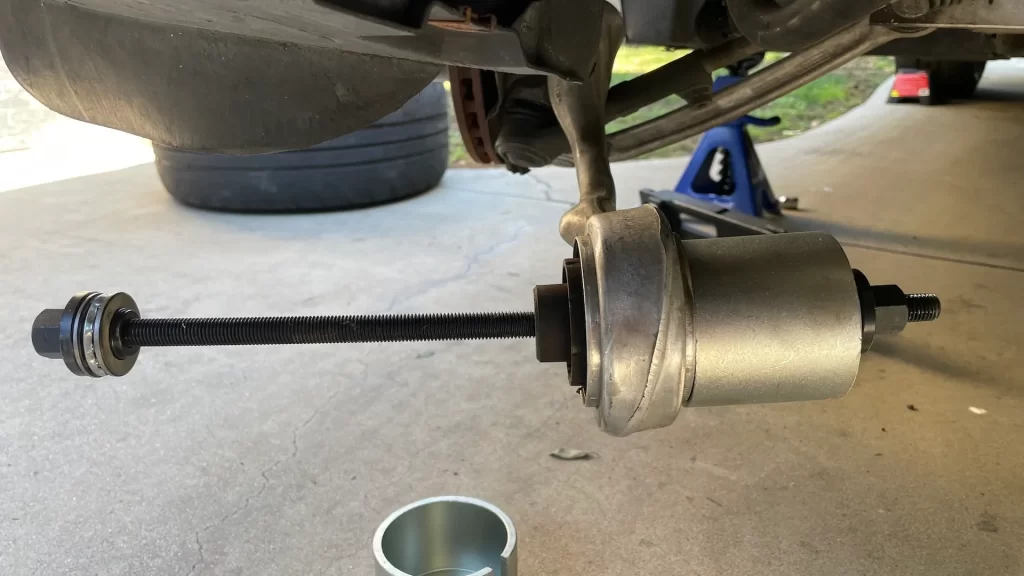

5. Frequently Asked Questions About Bushing Installation
Q1: Can I install bushings without a hydraulic press?
While a hydraulic press is the recommended tool for proper bushing installation, alternatives exist for specific situations. Threaded presses (such as ball joint presses) can be effective for smaller bushings, and in some cases, carefully driving the bushing in with a hammer and appropriately sized driver may work. However, these methods increase the risk of misalignment and damage. For precision applications and larger bushings, a hydraulic press remains the professional choice .
Q2: How do I know when a bushing needs replacement?
Common indicators for bushing replacement include: visible wear or cracking of the bushing material, increased vibration during operation, clunking or squeaking noises from joints, irregular tire wear (for automotive applications), and diminished handling precision. For precision applications, measure clearance with a dial indicator—excessive play often signals the need for replacement.
Q3: Is lubrication always required when installing bushings?
Lubrication requirements depend on the bushing material and type. Rubber bushings typically require no lubrication, while polyurethane and other polymer bushings definitely require lubrication with the specified compound to prevent binding and squeaking. For press-fit metal bushings, a light lubricant on the OD facilitates installation but shouldn’t be used with certain locking bushings where it might prevent proper seating .
Q4: What’s the most common mistake in bushing installation?
Misalignment during pressing is arguably the most frequent serious error. This can damage both the bushing and housing, leading to immediate failure or significantly reduced service life. Other common mistakes include failing to clean components thoroughly before installation, using improper tools that damage bushing surfaces, and incorrect torque application on fasteners for locking bushings.
Q5: How important is torque specification for bushing fasteners?
Extremely important. Under-torquing can allow bushings to loosen during operation, potentially causing catastrophic failure. Over-torquing can distort components, damage bushing flanges, and make future removal difficult. Always reference the manufacturer’s torque specifications rather than relying on instinct, and use a properly calibrated torque wrench for accuracy.
Q6: Can I reuse bushings once they’ve been removed?
In most cases, bushings should not be reused after removal. The removal process typically distorts or damages the bushing, compromising its structural integrity and performance capabilities. This is particularly true for press-fit bushings and those with precision interference fits. Always install new bushings during any service procedure.
Q7: Why is there a gap required on some bushing designs?
For split-taper and QD bushings, maintaining a gap between the component hub and bushing flange is essential for proper operation. This gap ensures the clamping force is properly distributed and allows the bushing to contract uniformly onto the shaft. Closing this gap during installation indicates incorrect installation and can lead to component failure.
Q8: How do I handle bushings for through-housing applications?
For through-housings, ensure the bushing is pressed in squarely to avoid misalignment. Use an alignment tool or appropriately sized socket to maintain perpendicular alignment during installation. For applications where multiple bushings must be aligned (such as hinge points), consider using an alignment bar during installation to ensure perfect bore alignment.
Q9: What should I do if a bushing starts cocking during pressing?
If a bushing begins to cock during pressing, stop immediately. Back off the press pressure, realign the bushing and drivers, then restart the pressing operation. Continuing to press a cocked bushing will likely damage both the bushing and housing, requiring expensive repairs or replacement of components.
Q10: Are there special considerations for installing self-lubricating bushings?
Yes, self-lubricating bushings like MYWAY’s DU/SF-1 series require specific handling. Avoid damaging the PTFE sliding surface during installation, and ensure lubrication grooves remain clear and unobstructed. These bushings typically should not be additionally lubricated unless specified by the manufacturer, as foreign lubricants can interfere with their self-lubricating properties .
MYWAY products can be tailored to your specific requirements.

