Recent Posts
What Are Bushings Used For?
Introduction: The Unsung Heroes of Mechanical Engineering
In the world of mechanical engineering and industrial machinery, bushings may be small components, but they play an enormous role in ensuring smooth operation and longevity. Often called plain bearings, sleeve bearings, or simply bushes, these cylindrical components serve as crucial interfaces between moving parts in countless applications across virtually every industry.
While they might not get the same attention as more complex mechanical components, bushings are fundamental to reducing friction, absorbing vibrations, and protecting more expensive machinery from wear and damage. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about bushings – from their basic functions and types to their applications and maintenance requirements.

Table of Contents
1. Understanding Bushings: More Than Just Simple Components
A bushing is fundamentally a cylindrical lining or sleeve designed to reduce friction between moving parts, typically between a rotating shaft and its stationary housing. Unlike rolling-element bearings that use balls or rollers, bushings operate on the principle of sliding friction, making them ideal for various applications where simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability are paramount.
2. Primary Functions and Applications
a. Friction Reduction and Wear Protection
Bushings create a low-friction interface between moving components, significantly reducing energy consumption and preventing direct metal-to-metal contact. This protective function extends the lifespan of both the rotating shaft and the housing, making bushings essentially sacrificial components that protect more valuable machinery parts.
b. Vibration Damping and Noise Reduction
Particularly in automotive and industrial applications, bushings made from materials like rubber or specialized polymers excel at absorbing vibrations and reducing operational noise. This capability is crucial for enhancing operator comfort and protecting sensitive equipment from harmonic vibrations.
c. Load Support and Alignment
Bushings provide essential support for radial and axial loads while maintaining proper alignment between components. Their robust construction allows them to handle significant stress while ensuring precise positioning of moving parts.
d. Electrical Insulation
In electrical applications, bushings serve as insulating barriers, preventing current flow between conductive components while allowing mechanical movement or connection.

3. Common Bushing Materials and Their Applications
CuSn8 and CuSn6 alloys offer excellent wear resistance and load-bearing capacity
Self-lubricating varieties with graphite plugs or oil impregnation
Ideal for heavy-duty applications in construction and agricultural equipment
High-strength options for extreme load conditions
Often used in automotive suspensions and industrial machinery
Can be hardened for additional wear resistance
Polymer and Composite Bushings
PTFE and Nylon bushings provide self-lubricating properties
Excellent corrosion resistance and electrical insulation
Suitable for food processing and chemical industries
Rubber Bushings
Superior vibration isolation and noise reduction
Common in automotive suspensions and mounting systems
Flexible design accommodates misalignment
4. Key Industries and Applications
Suspension systems and control arms
Engine mounts and transmission components
Steering linkages and brake systems
Industrial Machinery
Electric motors and pumps
Conveyor systems and material handling equipment
Machine tools and precision equipment
Construction and Heavy Equipment
Excavator pins and linkage systems
Crane and hoist mechanisms
Earth-moving equipment joints
Power Generation
Turbine components and generator systems
Transformer bushings and electrical insulation
Hydraulic systems and valve mechanisms
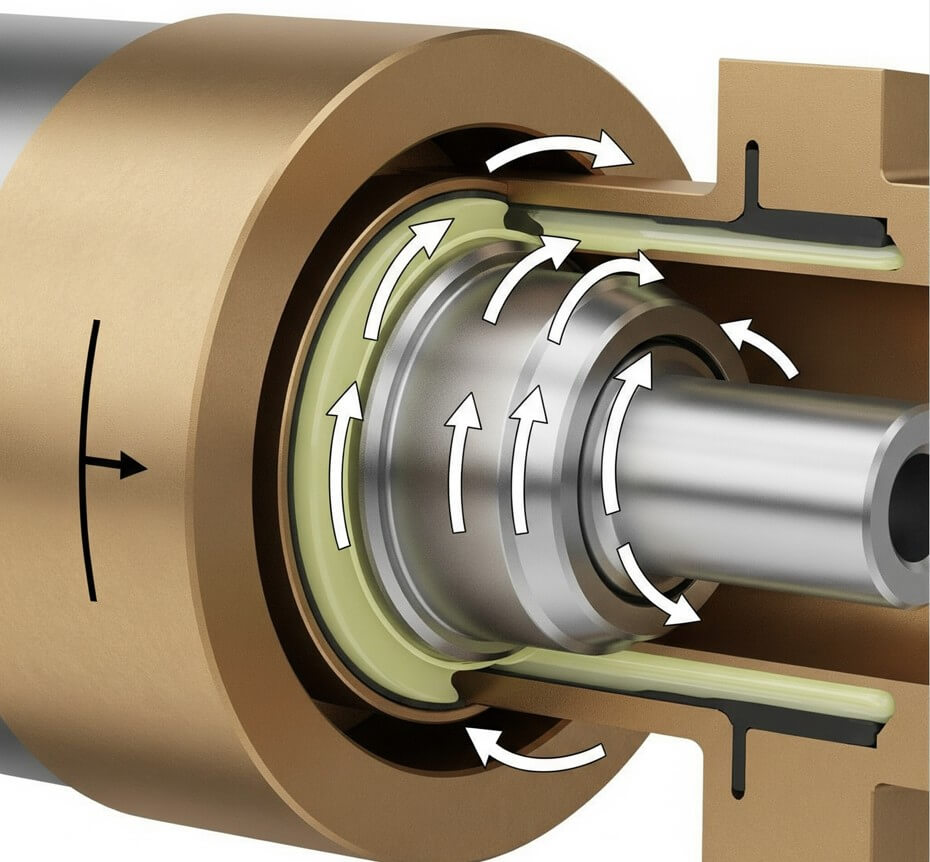
5. Bushing Selection Criteria
Choosing the right bushing requires careful consideration of several factors:
Load Requirements
Radial and axial load capacities
Static versus dynamic loading conditions
Shock load resistance
Environmental Conditions
Temperature ranges and thermal expansion
Exposure to chemicals, moisture, or contaminants
Corrosion resistance requirements
Operational Parameters
Rotational speeds and surface velocities
Lubrication availability and maintenance intervals
Expected service life and replacement frequency
6. Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for optimal bushing performance:
Installation Guidelines
Ensure proper clearance and interference fits
Use appropriate installation tools to prevent damage
Verify alignment before final assembly
Maintenance Protocols
Regular inspection for wear and damage
Proper lubrication schedules based on application
Monitoring for unusual noise or vibration
Common Failure Modes
Excessive wear from inadequate lubrication
Corrosion in harsh environments
Fatigue cracking under heavy cyclic loading
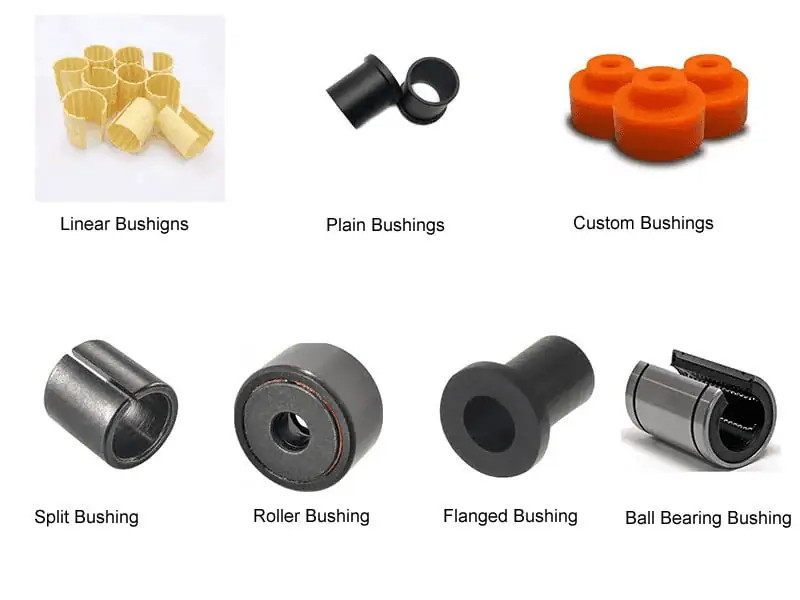

7. Why Choose MYWAY Bushings?
At MYWAY, we understand that bushing performance can make or break your machinery’s reliability. Our comprehensive range of bushings combines advanced materials with precision engineering to deliver unmatched performance in the most demanding applications.
Our Technical Expertise
Custom material formulations for specific application needs
Precision manufacturing to exacting tolerances
Comprehensive quality control and testing
Industry-Specific Solutions
Heavy-duty bushings for construction equipment
High-temperature variants for power generation
Corrosion-resistant options for marine applications
Value-Added Services
Technical consultation and engineering support
Custom design and rapid prototyping
Global logistics and supply chain management
8. Conclusion: Partner with MYWAY for Superior Bushing Solutions
Bushings may be small components, but their impact on machinery performance and reliability is enormous. Choosing the right bushing supplier can significantly affect your operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and equipment longevity.
MYWAY brings decades of engineering expertise and manufacturing excellence to every bushing we produce. Our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction makes us the preferred choice for industries worldwide.
Ready to optimize your machinery performance?
Contact MYWAY today for expert technical consultation, custom quoting, and engineering support. Let us help you find the perfect bushing solution for your specific application requirements.
Contact us today for technical specifications and pricing
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What’s the difference between bushings and bearings?
A: While both reduce friction between moving parts, bushings (plain bearings) operate on sliding friction principles, while bearings typically use rolling elements. Bushings are generally simpler, more cost-effective, and better for lower-speed, higher-load applications.
Q2: How often should bushings be replaced?
A: Replacement intervals depend on operating conditions, loads, and maintenance practices. Regular inspections should check for excessive wear, cracking, or deformation. MYWAY provides specific maintenance guidelines for each bushing type.
Q3: Can MYWAY produce custom bushings for special applications?
A: Absolutely. We specialize in custom solutions, including special materials, unique geometries, and application-specific features. Our engineering team works directly with clients to develop optimal bushing solutions.
Q4: What lubrication do MYWAY bushings require?
A: Requirements vary by material and application. We offer self-lubricating options, oil-impregnated bronze bushings, and designs for grease lubrication. Our technical team provides specific lubrication recommendations for each application.
Q5: How do I select the right bushing material for my application?
A: Consider factors like load capacity, speed, temperature, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements. MYWAY‘s engineering team can help analyze your specific needs and recommend the optimal material solution.
MYWAY products can be tailored to your specific requirements.

